'Analogy-Based Comprehensive Diabetes Education' (ABCDE) Improves Glycemic Control of Diabetic Patients in an Underserved Population: Results of a Retrospective Chart Analysis
- PMID: 35326887
- PMCID: PMC8953270
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare10030409
'Analogy-Based Comprehensive Diabetes Education' (ABCDE) Improves Glycemic Control of Diabetic Patients in an Underserved Population: Results of a Retrospective Chart Analysis
Abstract
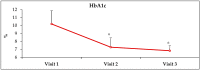
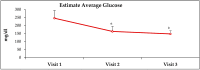
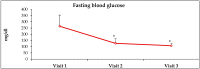
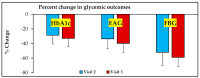
Diabetes is the leading global cause for blindness, kidney failure and amputations. Preventing these complications requires optimal glycemic control, and it is imperative that diabetic patients understand the fundamental concepts of diabetes care. Although patients attend formal diabetes education classes, many do not comprehend basic concepts of diabetes, and are often noncompliant with diet, exercise and medications. A novel approach termed 'analogy-based comprehensive diabetes education' (ABCDE) was developed to educate HIV-patients with diabetes about basic concepts of diabetes care. The object of this manuscript is to report the results of a retrospective chart review on the impact of ABCDE on glycemic outcomes in 24 patients who had failed usual care (including formal diabetes education, physician visits, and diabetic medications), and were non-adherent with diet and medications. They received only the ABCDE without any changes in pharmacotherapy. The impact on glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and fasting blood glucose (FBG) was assessed at subsequent visits. HbA1c was found to decline by 22% and 33% after 3 and 6 months, respectively, with corresponding declines in FBG by 53% and 59%, respectively. These results suggest that ABCDE in outpatient diabetes clinics could be effective in behavior modification toward improving glycemic control, and warrants additional investigation.
Keywords: analogies; diabetes; education; glycemic outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Mobile-Based Intervention for Glycemic Control in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: Retrospective, Propensity Score-Matched Cohort Study.JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020 Mar 11;8(3):e15390. doi: 10.2196/15390. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth. 2020. PMID: 32159518 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Group Patient Education on Glycemic Control Among People Living with Type 2 Diabetes in Vietnam: A Randomized Controlled Single-Center Trial.Diabetes Ther. 2021 May;12(5):1503-1521. doi: 10.1007/s13300-021-01052-8. Epub 2021 Apr 11. Diabetes Ther. 2021. PMID: 33840068 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise and Postprandial Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2016;12(3):199-210. doi: 10.2174/1573399811666150615112441. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2016. PMID: 26073704 Review.
-
The Effectiveness of Motivational Interviewing on Glycemic Control for Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (DM2): A Systematic Review.JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012;10(42 Suppl):1-17. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2012-246. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2012. PMID: 27820150
-
Rapid-Acting Insulin Analogues Versus Regular Human Insulin: A Meta-Analysis of Effects on Glycemic Control in Patients with Diabetes.Diabetes Ther. 2020 Mar;11(3):573-584. doi: 10.1007/s13300-019-00732-w. Epub 2019 Dec 23. Diabetes Ther. 2020. PMID: 31873857 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chronic disease management program applied to type 2 diabetes patients and prevention of diabetic complications: a retrospective cohort study using nationwide data.BMC Public Health. 2023 May 23;23(1):928. doi: 10.1186/s12889-023-15763-z. BMC Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37221526 Free PMC article.
References
-
- [(accessed on 21 December 2021)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/diabetes.
-
- Williams R., Karuranga S., Malanda B., Saeedi P., Basit A., Besançon S., Bommer C., Esteghamati A., Ogurtsova K., Zhang P., et al. Global and regional estimates and projections of diabetes-related health expenditure: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020;162:108072. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108072. - DOI - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association Standards of Care and Diabetes Guidelines. [(accessed on 20 December 2021)];Diab Care. 2021 44((Suppl. 1)) Available online: https://diabetesjournals.org/care/issue/44/Supplement_1.
-
- [(accessed on 21 December 2021)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/chp/knowledge/publications/adherence_full_report.pdf....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

