COVID-19 Pneumonia Classification Based on NeuroWavelet Capsule Network
- PMID: 35326900
- PMCID: PMC8949056
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare10030422
COVID-19 Pneumonia Classification Based on NeuroWavelet Capsule Network
Abstract
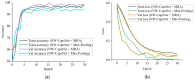
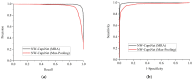
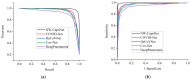
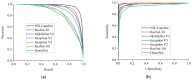
Since it was first reported, coronavirus disease 2019, also known as COVID-19, has spread expeditiously around the globe. COVID-19 must be diagnosed as soon as possible in order to control the disease and provide proper care to patients. The chest X-ray (CXR) has been identified as a useful diagnostic tool, but the disease outbreak has put a lot of pressure on radiologists to read the scans, which could give rise to fatigue-related misdiagnosis. Automatic classification algorithms that are reliable can be extremely beneficial; however, they typically depend upon a large amount of COVID-19 data for training, which are troublesome to obtain in the nick of time. Therefore, we propose a novel method for the classification of COVID-19. Concretely, a novel neurowavelet capsule network is proposed for COVID-19 classification. To be more precise, first, we introduce a multi-resolution analysis of a discrete wavelet transform to filter noisy and inconsistent information from the CXR data in order to improve the feature extraction robustness of the network. Secondly, the discrete wavelet transform of the multi-resolution analysis also performs a sub-sampling operation in order to minimize the loss of spatial details, thereby enhancing the overall classification performance. We examined the proposed model on a public-sourced dataset of pneumonia-related illnesses, including COVID-19 confirmed cases and healthy CXR images. The proposed method achieves an accuracy of 99.6%, sensitivity of 99.2%, specificity of 99.1% and precision of 99.7%. Our approach achieves an up-to-date performance that is useful for COVID-19 screening according to the experimental results. This latest paradigm will contribute significantly in the battle against COVID-19 and other diseases.
Keywords: COVID-19; capsule network; chest X-ray; convolutional neural network; pneumonia; wavelet.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
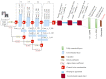
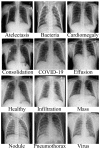
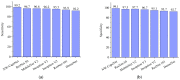
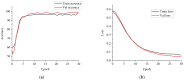
Similar articles
-
COVID-19 Diagnosis from Chest X-ray Images Using a Robust Multi-Resolution Analysis Siamese Neural Network with Super-Resolution Convolutional Neural Network.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Mar 18;12(3):741. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12030741. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35328294 Free PMC article.
-
WMR-DepthwiseNet: A Wavelet Multi-Resolution Depthwise Separable Convolutional Neural Network for COVID-19 Diagnosis.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Mar 21;12(3):765. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12030765. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35328318 Free PMC article.
-
Fine-Tuned Siamese Network with Modified Enhanced Super-Resolution GAN Plus Based on Low-Quality Chest X-ray Images for COVID-19 Identification.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Mar 15;12(3):717. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12030717. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35328271 Free PMC article.
-
A novel COVID diagnosis and feature extraction based on discrete wavelet model and classification using X-ray and CT images.Multimed Tools Appl. 2023 Jan 21:1-42. doi: 10.1007/s11042-023-14367-4. Online ahead of print. Multimed Tools Appl. 2023. PMID: 36712955 Free PMC article.
-
Conv-CapsNet: capsule based network for COVID-19 detection through X-Ray scans.Multimed Tools Appl. 2023 Feb 21:1-25. doi: 10.1007/s11042-023-14353-w. Online ahead of print. Multimed Tools Appl. 2023. PMID: 36846527 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Screening Lung Diseases Using Cascaded Feature Generation and Selection Strategies.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Jul 14;10(7):1313. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10071313. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35885839 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges of deep learning methods for COVID-19 detection using public datasets.Inform Med Unlocked. 2022;30:100945. doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2022.100945. Epub 2022 Apr 12. Inform Med Unlocked. 2022. PMID: 35434261 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 Diagnosis from Chest X-ray Images Using a Robust Multi-Resolution Analysis Siamese Neural Network with Super-Resolution Convolutional Neural Network.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Mar 18;12(3):741. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12030741. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35328294 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard with Vaccination Data. [(accessed on 12 August 2021)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
-
- Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center COVID-19 Map. [(accessed on 16 September 2021)]. Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

