Effects of Electrical Stimulation of Acupoints on Xerostomia for Patients Who Undergo Hemodialysis
- PMID: 35326976
- PMCID: PMC8954393
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare10030498
Effects of Electrical Stimulation of Acupoints on Xerostomia for Patients Who Undergo Hemodialysis
Abstract
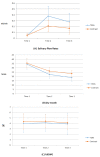
Xerostomia plays a major role in higher interdialytic weight gain (IDWG), which causes cardiovascular complications in patients who undergo hemodialysis. However, few studies have determined a method to manage xerostomia. This study determines the effect of transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation (TEAS) on hemodialysis patients with xerostomia and the percentage of IDWG. The study was a single-blind and quasi-experimental study. There are 75 participants: 37 in the TEAS group and 38 in the contrast group. The TEAS group used 250 µs and 50 Hz and the contrast group used 50 µs and 2 Hz three times a week for 3 weeks to stimulate ST 6 and TE17 acupoints. The salivary flow rates, dry mouth, and %IDWG were determined before, during and one week after the program. Compared with the contrast group, the TEAS group showed a significantly improved salivary flow rate (mL/min) (F (2, 123) = 15.28, p < 0.0001), and patients recovered their normal salivary flow rate. However, the results show that both groups showed significant improvement in dry mouth after treatment. The TEAS group demonstrated no effect in terms of %IDWG, as expected. The results show that a TEAS program is an effective means of symptom management for xerostomia patients who undergo hemodialysis. A TEAS program can be used to manage symptoms for xerostomia patients who undergo hemodialysis.
Keywords: acupoints; hemodialysis; interdialytic weight gain; salivary flow rates; xerostomia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation on increasing salivary flow rate in hemodialysis patients.Oral Dis. 2019 Jan;25(1):133-141. doi: 10.1111/odi.12948. Epub 2018 Sep 9. Oral Dis. 2019. PMID: 30076692 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of the Combination of Auricular Acupressure and a Fluid-Restriction Adherence Program on Salivary Flow Rate, Xerostomia, Fluid Control, Interdialytic Weight Gain, and Diet-Related Quality of Life in Patients Undergoing Hemodialysis.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Oct 7;18(19):10520. doi: 10.3390/ijerph181910520. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34639819 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased salivary flow rate as a dipsogenic factor in hemodialysis patients: evidence from an observational study and a pilocarpine clinical trial.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005 Nov;16(11):3418-29. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2005040346. Epub 2005 Sep 21. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005. PMID: 16177001 Clinical Trial.
-
Xerostomia in patients on chronic hemodialysis: An update.Semin Dial. 2019 Sep;32(5):467-474. doi: 10.1111/sdi.12821. Epub 2019 May 22. Semin Dial. 2019. PMID: 31117154 Review.
-
Thirst in patients on chronic hemodialysis: What do we know so far?Int Urol Nephrol. 2020 Apr;52(4):697-711. doi: 10.1007/s11255-020-02401-5. Epub 2020 Feb 25. Int Urol Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 32100204 Review.
Cited by
-
A scoping review on hyposalivation associated with systemic conditions: the role of physical stimulation in the treatment approaches.BMC Oral Health. 2023 Jul 21;23(1):505. doi: 10.1186/s12903-023-03192-8. BMC Oral Health. 2023. PMID: 37480103 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saad T.F., Hentschel D.M., Koplan B., Wasse H., Asif A., Patel D.V., Salman L., Carrillo R., Hoggard J. Cardiovascular implantable electronic device leads in CKD and ESRD patients: Review and recommendations for practice. Semin. Dial. 2013;26:114–123. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-139X.2012.01103.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Khalil A.A., Darawad M., Al Gamal E., Hamdan-Mansour A.M., Abed M.A. Predictors of dietary and fluid non-adherence in Jordanian patients with end-stage renal disease receiving haemodialysis: A cross-sectional study. J. Clin. Nurs. 2013;22:127–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2702.2012.04117.x. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources