Effects of Animal-Assisted Therapy (AAT) in Alzheimer's Disease: A Case Study
- PMID: 35327045
- PMCID: PMC8950375
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare10030567
Effects of Animal-Assisted Therapy (AAT) in Alzheimer's Disease: A Case Study
Abstract
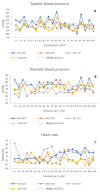
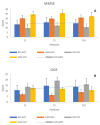
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder, characterized by cortical dementia and irreversibly progressive developments leading to a vegetative state and, finally, to death. Although many aspects of its etiology, diagnosis and treatment still remain obscure and the current approach to the disease mostly suffers from limited and low-efficiency therapeutic means, nevertheless, recent interventions have aimed at improving patients' quality of life through nonpharmacological approaches, including animal-assisted therapy (AAT), arousing growing interest. In order to assess the physiological and neuropsychological effects of AAT on AD, 24 residents of a rest house in northern Italy were enrolled. The intervention consisted of one 45-minute AAT session per week over ten weeks. Twelve residents (six AD and six non-AD) received AAT and twelve (six AD and six non-AD) were controls. In order to evaluate the physiological and clinical effect of AAT on AD residents, three cardiac parameters, including the systolic and diastolic blood pressure and heart rate, were measured. Moreover, the neurocognitive and depressive states were assessed by the Mini Mental State Examination and the Geriatric Depression Scale, respectively. Analyses were performed by a four-way ANOVA model (including two ways for repeated measures) considering each main effect and interaction possible in the design. Our findings, despite the small sample size, suggest that AAT has a positive significant effect on physiological parameters and neurocognitive impairment, while no effect was observed on the depression level.
Keywords: GDS; MMSE; cognitive and behavioral interventions; heart rate; neurodegenerative disorders; systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the efficacy of animal-assisted therapy based on the reality orientation therapy protocol in Alzheimer's disease patients: a pilot study.Psychogeriatrics. 2016 Jul;16(4):240-6. doi: 10.1111/psyg.12145. Epub 2015 Sep 15. Psychogeriatrics. 2016. PMID: 26370064
-
Animal-Assisted Therapy as a Non-Pharmacological Approach in Alzheimer's Disease: A Retrospective Study.Animals (Basel). 2020 Jul 6;10(7):1142. doi: 10.3390/ani10071142. Animals (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32640648 Free PMC article.
-
[Impact of animal-assisted therapy on well-being in patients with Alzheimer's disease (ELIAUT study)].Geriatr Psychol Neuropsychiatr Vieil. 2023 Dec 1;21(4):506-516. doi: 10.1684/pnv.2023.1134. Geriatr Psychol Neuropsychiatr Vieil. 2023. PMID: 38269565 Clinical Trial. French.
-
Animal-Assisted Therapy in Elderly Patients: Evidence and Controversies in Dementia and Psychiatric Disorders and Future Perspectives in Other Neurological Diseases.J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 2018 May;31(3):149-157. doi: 10.1177/0891988718774634. Epub 2018 May 15. J Geriatr Psychiatry Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29764282 Review.
-
[Awareness disorders in Alzheimer's disease and in mild cognitive impairment].Encephale. 2014 Apr;40(2):180-7. doi: 10.1016/j.encep.2013.10.003. Epub 2014 Mar 11. Encephale. 2014. PMID: 24630532 Review. French.
Cited by
-
A bibliometric study for global hotspots and trends in animal-assisted interventions (1983-2023).Front Psychiatry. 2025 Apr 16;16:1490122. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1490122. eCollection 2025. Front Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40309502 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cibeira N., Maseda A., Lorenzo-López L., González-Abraldes I., López-López R., Rodríguez-Villamil J.L., Millán-Calenti J.C. Bright Light Therapy in Older Adults with Moderate to Very Severe Dementia: Immediate Effects on Behavior, Mood, and Physiological Parameters. Healthcare. 2021;9:1065. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9081065. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

