Dynamic miRNA Landscape Links Mammary Gland Development to the Regulation of Milk Protein Expression in Mice
- PMID: 35327124
- PMCID: PMC8944794
- DOI: 10.3390/ani12060727
Dynamic miRNA Landscape Links Mammary Gland Development to the Regulation of Milk Protein Expression in Mice
Abstract
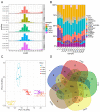
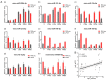
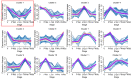
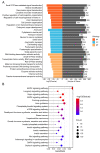
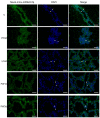
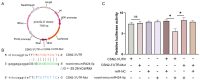
Mammary gland morphology varies considerably between pregnancy and lactation status, e.g., virgin to pregnant and lactation to weaning. Throughout these critical developmental phases, the mammary glands undergo remodeling to accommodate changes in milk production capacity, which is positively correlated with milk protein expression. The purpose of this study was to investigate the microRNA (miRNA) expression profiles in female ICR mice's mammary glands at the virgin stage (V), day 16 of pregnancy (P16d), day 12 of lactation (L12d), day 1 of forced weaning (FW1d), and day 3 of forced weaning (FW3d), and to identify the miRNAs regulating milk protein gene expression. During the five stages of testing, 852 known miRNAs and 179 novel miRNAs were identified in the mammary glands. Based on their expression patterns, the identified miRNAs were grouped into 12 clusters. The expression pattern of cluster 1 miRNAs was opposite to that of milk protein genes in mammary glands in all five different stages. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analyses revealed that the predicted target genes of cluster 1 miRNAs were related to murine mammary gland development and lactation. Furthermore, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) analysis revealed that the novel-mmu-miR424-5p, which belongs to the cluster 1 miRNAs, was expressed in murine mammary epithelial cells. The dual-luciferase reporter assay revealed that an important milk protein gene-β-casein (CSN2)-was regarded as one of the likely targets for the novel-mmu-miR424-5p. This study analyzed the expression patterns of miRNAs in murine mammary glands throughout five critical developmental stages, and discovered a novel miRNA involved in regulating the expression of CSN2. These findings contribute to an enhanced understanding of the developmental biology of mammary glands, providing guidelines for increasing lactation efficiency and milk quality.
Keywords: mammary gland; microRNA; milk protein; mouse.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hormonal regulation of miRNA during mammary gland development.Biol Open. 2024 Jun 15;13(6):bio060308. doi: 10.1242/bio.060308. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Biol Open. 2024. PMID: 38712984 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of microRNA profiles in the mammary gland tissue of dairy goats at the late lactation, dry period and late gestation stages.PLoS One. 2020 Jun 8;15(6):e0234427. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234427. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32511270 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Dynamic Landscape during Mouse Mammary Gland Development from Virgin to Pregnant, Lactating, and Involuting Stages.J Agric Food Chem. 2024 Apr 3;72(13):7546-7557. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c09647. Epub 2024 Mar 21. J Agric Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 38513219 Review.
-
Characterisation of microRNA expression in post-natal mouse mammary gland development.BMC Genomics. 2009 Nov 20;10:548. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-548. BMC Genomics. 2009. PMID: 19930549 Free PMC article.
-
[Progress on the miRNA related with mammary gland development and lactation].Yi Chuan. 2013 Jun;35(6):695-702. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1005.2013.00695. Yi Chuan. 2013. PMID: 23774014 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
In Vitro Screening of Trehalose Synbiotics and Their Effects on Early-Lactating Females and Offspring Mice.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Oct 11;13(10):1223. doi: 10.3390/antiox13101223. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39456476 Free PMC article.
-
Alfalfa xeno-miR159a regulates bovine mammary epithelial cell proliferation and milk protein synthesis by targeting PTPRF.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 20;14(1):9117. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-59948-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38643232 Free PMC article.
-
Periconceptional and Prenatal Exposure to Metals and Extracellular Vesicle and Particle miRNAs in Human Milk: A Pilot Study.Expo Health. 2023 Dec;15(4):731-743. doi: 10.1007/s12403-022-00520-1. Epub 2022 Nov 3. Expo Health. 2023. PMID: 38074282 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: Role of Non-Coding RNAs in Animals.Animals (Basel). 2023 Feb 23;13(5):805. doi: 10.3390/ani13050805. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36899662 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of Pregnancy on Whole-Transcriptome Sequencing in the Mammary Gland of Kazakh Mares.Animals (Basel). 2025 Jul 11;15(14):2056. doi: 10.3390/ani15142056. Animals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40723519 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

