Successful Laparoscopic Oviductal Artificial Insemination in the Endangered Tsushima Leopard Cat (Prionailurus bengalensis euptilurus)
- PMID: 35327174
- PMCID: PMC8944764
- DOI: 10.3390/ani12060777
Successful Laparoscopic Oviductal Artificial Insemination in the Endangered Tsushima Leopard Cat (Prionailurus bengalensis euptilurus)
Abstract
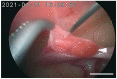
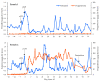
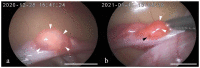
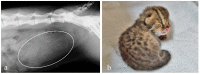
The Tsushima leopard cat (Prionailurus bengalensis euptilurus) is an endangered wild felid that lives solely on Tsushima Island, Nagasaki, Japan. Japan's Ministry of the Environment is working with the Japanese Association of Zoo and Aquariums for ex situ conservation of this species. However, considering genetic diversity, it is difficult to conduct captive breeding programs by natural breeding alone; hence, assisted reproductive technologies are required. This study aimed to breed Tsushima leopard cats, which otherwise cannot be paired, using laparoscopic oviductal artificial insemination (AI). Female Tsushima leopard cats (female 1, aged 7 years; female 2, aged 6 years) were treated with 200 IU equine chorionic gonadotropin, followed by administration of 1000 IU porcine luteinizing hormone (pLH) after 96 h to induce ovulation. Laparoscopic AI was performed 32 h post-pLH administration. Females 1 and 2 were inseminated in the oviduct with 2.4 × 10⁶ and 3.3 × 10⁶ motile spermatozoa, respectively, collected from two males. Pregnancy was confirmed by radiography 45 and 51 days post-AI in females 1 and 2, respectively; one fetus was found in female 2. Moreover, female 2 had spontaneous delivery of a female kitten 66 days post-AI. This is the first successful case of AI in a Tsushima leopard cat.
Keywords: Tsushima leopard cat; equine chorionic gonadotropin; ex situ conservation; laparoscopic oviductal artificial insemination; porcine luteinizing hormone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neoplasia in captive Tsushima leopard cats (Prionailurus bengalensis euptilurus).J Comp Pathol. 2023 Jul;204:11-16. doi: 10.1016/j.jcpa.2023.05.004. Epub 2023 Jun 12. J Comp Pathol. 2023. PMID: 37315404
-
SUCCESSFUL LAPAROSCOPIC OVIDUCTAL ARTIFICIAL INSEMINATION IN THE CLOUDED LEOPARD (NEOFELIS NEBULOSA) IN THAILAND.J Zoo Wildl Med. 2017 Sep;48(3):804-812. doi: 10.1638/2016-0287.1. J Zoo Wildl Med. 2017. PMID: 28920796
-
Laparoscopic oviductal artificial insemination improves pregnancy success in exogenous gonadotropin-treated domestic cats as a model for endangered felids.Biol Reprod. 2013 Jul 5;89(1):4. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.112.105353. Print 2013 Jul. Biol Reprod. 2013. PMID: 23699391 Free PMC article.
-
Laparoscopic oviductal embryo transfer and artificial insemination in felids--challenges, strategies and successes.Reprod Domest Anim. 2012 Dec;47 Suppl 6(Suppl 6):136-40. doi: 10.1111/rda.12069. Reprod Domest Anim. 2012. PMID: 23279483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Female reproductive cycles of wild female felids.Anim Reprod Sci. 2011 Apr;124(3-4):155-62. doi: 10.1016/j.anireprosci.2010.08.024. Epub 2010 Sep 3. Anim Reprod Sci. 2011. PMID: 20888156 Review.
Cited by
-
Fecal Glucocorticoid Metabolites as a Noninvasive Indicator of Stress in the Tsushima Leopard Cats (Prionailurus bengalensis euptilurus): Application to Health Care.Animals (Basel). 2022 Apr 21;12(9):1072. doi: 10.3390/ani12091072. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35565499 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of cauda epididymal sperm immediately after collection and after freezing-thawing from Amur leopard cats (Prionailurus bengalensis euptilurus) and a local population of the subspecies Tsushima leopard cats.J Vet Med Sci. 2023 Jan 20;85(1):117-122. doi: 10.1292/jvms.22-0230. Epub 2022 Nov 28. J Vet Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 36436949 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Izawa M., Doi T., Nakanishi N., Teranishi A. Ecology and Conservation of Two Endangered Subspecies of the Leopard Cat (Prionailurus bengalensis) on Japanese Islands. Biol. Conserv. 2009;142:1884–1890. doi: 10.1016/j.biocon.2009.05.005. - DOI
-
- Machii J., Monji K., Imada R., Tanaka S., Nagao E., Saito Y., Hamachi M. Husbandry and Breeding of the Tsushima Leopard Cat, Felis bengalensis euptilura. J Jpn. Assoc. Zool. Aquat. 2002;43:94–103. (In Japanese)
-
- Dresser B.L., Kramer L., Reece B., Russell P.T. Induction of ovulation and successful artificial insemination in a Persian leopard (Panthera pardus saxicolor) Zoo Biol. 1982;1:55–57. doi: 10.1002/zoo.1430010106. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

