Screening and Identification of Putative Long Non-Coding RNA in Childhood Obesity: Evaluation of Their Transcriptional Levels
- PMID: 35327332
- PMCID: PMC8945364
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10030529
Screening and Identification of Putative Long Non-Coding RNA in Childhood Obesity: Evaluation of Their Transcriptional Levels
Abstract
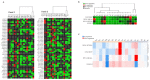
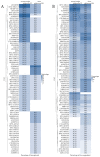
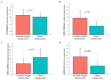
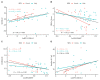
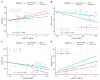
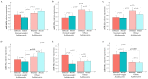
Background and Methods: Long non-coding RNAs (LncRNAs) and microRNAs are involved in the pathogenesis of obesity, a multifactorial disease that is characterized by inflammation, cardiometabolic complications, and increased cancer risk among other co-morbidities. The up/down regulation of LncRNAs and microRNAs may play an important role in this condition to identify new diagnostic/prognostic markers. The aim of the study was to identify circulating inflammatory LncRNAs in obese adolescents (n = 54) and to evaluate whether their expression behaved differently compared to normal-weight adolescents (n = 26). To have a more complete insight, the expression of some circulating miRNAs that are linked to obesity (miR-33a, miR-223, miR-142, miR-199a, miR-181a, and miR-4454) were also analyzed. Results: LncRNAs and miRNAs were extracted simultaneously from plasma samples and amplified by Real-Time PCR. Among the 86 LncRNAs that were analyzed with custom pre-designed plates, only four (RP11-347E10.1, RP11-10K16.1, LINC00657, and SNHG12) were amplified in both normal-weight and obese adolescents and only SNHG12 showed significantly lower expression compared to the normal-weight adolescents (p = 0.026). Circulating miRNAs showed a tendency to increase in obese subjects, except for miR-181a expression. LncRNAs and miRNAs correlated with some clinical and metabolic parameters. Conclusions: Our results suggest the importance of these new biomarkers to better understand the molecular mechanisms of childhood obesity and its metabolic disorder.
Keywords: LncRNAs; Real-Time PCR; biomarkers; childhood obesity; miRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circulating and Exosomal microRNA-33 in Childhood Obesity.Biomedicines. 2023 Aug 18;11(8):2295. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11082295. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37626791 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating microRNAs associated with C-type natriuretic peptide in childhood obesity.Peptides. 2020 Nov;133:170387. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2020.170387. Epub 2020 Aug 20. Peptides. 2020. PMID: 32828851
-
Long non-coding RNA HCP5 serves as a ceRNA sponging miR-17-5p and miR-27a/b to regulate the pathogenesis of childhood obesity via the MAPK signaling pathway.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2019 Dec 18;32(12):1327-1339. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2018-0432. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2019. PMID: 31622249
-
Circulating microRNAs and long non-coding RNAs in gastric cancer diagnosis: An update and review.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Sep 14;21(34):9863-86. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i34.9863. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26379393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating miRNAs as Biomarkers of Obesity and Obesity-Associated Comorbidities in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review.Nutrients. 2019 Nov 27;11(12):2890. doi: 10.3390/nu11122890. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31783635 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Circulating and Exosomal microRNA-33 in Childhood Obesity.Biomedicines. 2023 Aug 18;11(8):2295. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11082295. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37626791 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of circulating microRNAs in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis in young patients with obesity.Physiol Res. 2024 Dec 31;73(S3):S755-S769. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.935467. Physiol Res. 2024. PMID: 39808176 Free PMC article.
-
Biofluid-Derived Exosomal LncRNAs: Their Potential in Obesity and Related Comorbidities.Biology (Basel). 2024 Nov 26;13(12):976. doi: 10.3390/biology13120976. Biology (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39765643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of dietary rumen-protected glucose level and taurine supplementation on weight change and oxidative stress state of yaks after transport.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Nov 21;11:1492747. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1492747. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39641099 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Exosomal Coding and Non-Coding RNA Signature in Obese Adolescents.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 21;24(1):139. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010139. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36613584 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lifshitz F., Lifshitz J.Z. Globesity: The root causes of the obesity epidemic in the USA and now worldwide. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Rev. 2014;12:17–34. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

