Trends in Prediabetes and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Associated with Abdominal Obesity among Korean Children and Adolescents: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey between 2009 and 2018
- PMID: 35327390
- PMCID: PMC8945340
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10030584
Trends in Prediabetes and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Associated with Abdominal Obesity among Korean Children and Adolescents: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey between 2009 and 2018
Abstract
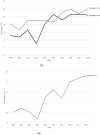
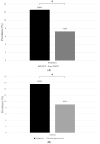
Investigations on the trends of prediabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) among children are scarce. We aimed to analyze the trends of prediabetes and NAFLD, as well as their association, among Korean children and adolescents from 2009 to 2018. This study investigated the prevalence of prediabetes, NAFLD, and abdominal obesity among 6327 children and adolescents aged 10-18 years according to age, sex, and body mass index (BMI) using a nationally representative survey. The prevalence of prediabetes, NAFLD, and abdominal obesity increased from 5.14%, 8.17%, and 5.97% respectively, in 2009 to 10.46%, 12.05%, and 10.51% respectively, in 2018. In age-specific analyses, an adverse trend in NAFLD was significant only in participants aged 16-18 years while the prevalence of prediabetes worsened significantly in all age groups. In BMI-specific analyses, the prevalence of prediabetes and NAFLD increased significantly only in participants with normal BMI. In logistic regression analysis, the odds ratio of prediabetes for NAFLD was 1.85 and those of abdominal obesity for prediabetes and NAFLD was 1.85 and 9.34, respectively. Our results demonstrated that the prevalence of prediabetes and NAFLD was increasing in association with abdominal obesity in Korean children and adolescents.
Keywords: adolescent; child; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; prediabetic state; prevalence; trend.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Zhu Y., Sidell M.A., Arterburn D., Daley M.F., Desai J., Fitzpatrick S.L., Horberg M.A., Koebnick C., McCormick E., Oshiro C., et al. Racial/ethnic disparities in the prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes by bmi: Patient outcomes research to advance learning (portal) multisite cohort of adults in the U.S. Diabetes Care. 2019;42:2211–2219. doi: 10.2337/dc19-0532. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vos M.B., Abrams S.H., Barlow S.E., Caprio S., Daniels S.R., Kohli R., Mouzaki M., Sathya P., Schwimmer J.B., Sundaram S.S., et al. Naspghan clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in children: Recommendations from the expert committee on nafld (econ) and the north american society of pediatric gastroenterology, hepatology and nutrition (naspghan) J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2017;64:319–334. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nobili V., Mantovani A., Cianfarani S., Alisi A., Mosca A., Sartorelli M.R., Maffeis C., Loomba R., Byrne C.D., Targher G. Prevalence of prediabetes and diabetes in children and adolescents with biopsy-proven non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2019;71:802–810. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.06.023. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

