The Interplay of Cx26, Cx32, Cx37, Cx40, Cx43, Cx45, and Panx1 in Inner-Ear Development of Yotari (dab1-/-) Mice and Humans
- PMID: 35327391
- PMCID: PMC8945117
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10030589
The Interplay of Cx26, Cx32, Cx37, Cx40, Cx43, Cx45, and Panx1 in Inner-Ear Development of Yotari (dab1-/-) Mice and Humans
Abstract
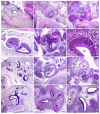
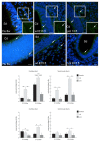
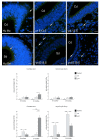
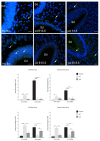
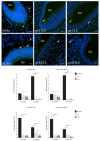
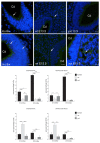
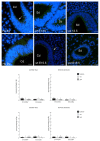
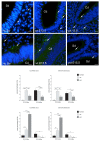
We investigated DAB1-protein deficiency in the inner-ear development of yotari in comparison to humans and wild-type (wt) mice by immunofluorescence for the expression of connexins (Cxs) and the pannexin Panx1. The spatial and temporal dynamics of Cx26, Cx32, Cx37, Cx40, Cx43, Cx45, and Panx1 were determined in the sixth and eighth weeks of human development and at the corresponding mouse embryonic E13.5 and E15.5, in order to examine gap junction intercellular communication (GJIC) and hemichannel formation. The quantification of the area percentage covered by positive signal was performed for the epithelium and mesenchyme of the cochlear and semicircular ducts and is expressed as the mean ± SD. The data were analysed by one-way ANOVA. Almost all of the examined Cxs were significantly decreased in the cochlear and semicircular ducts of yotari compared to wt and humans, except for Cx32, which was significantly higher in yotari. Cx40 dominated in human inner-ear development, while yotari and wt had decreased expression. The Panx1 expression in yotari was significantly lower than that in the wt and human inner ear, except at E13.5 in the mesenchyme of the wt and epithelium and mesenchyme of humans. Our results emphasize the relevance of GJIC during the development of vestibular and cochlear functions, where they can serve as potential therapeutic targets in inner-ear impairments.
Keywords: Cx26; Cx32; Cx37; Cx40; Cx43; Cx45; Panx1; gap junction; inner-ear development; yotari.
Conflict of interest statement
On behalf of all the authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Connexin Expression Is Altered in the Eye Development of Yotari Mice: A Preliminary Study.Biomolecules. 2024 Sep 19;14(9):1174. doi: 10.3390/biom14091174. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39334940 Free PMC article.
-
Connexin Expression Is Altered in Liver Development of Yotari (dab1 -/-) Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 2;22(19):10712. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910712. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34639052 Free PMC article.
-
Alteration of Cx37, Cx40, Cx43, Cx45, Panx1, and Renin Expression Patterns in Postnatal Kidneys of Dab1-/- (yotari) Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 28;22(3):1284. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031284. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33525532 Free PMC article.
-
Gap junctions and the connexin protein family.Cardiovasc Res. 2004 May 1;62(2):228-32. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2003.11.013. Cardiovasc Res. 2004. PMID: 15094343 Review.
-
Connexin expression in the retina.Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2000 Apr;32(1):138-45. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0173(99)00074-0. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 2000. PMID: 10751663 Review.
Cited by
-
The Expression of Connexin 37, 40, 43, 45 and Pannexin 1 in the Early Human Retina and Choroid Development and Tumorigenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 25;23(11):5918. doi: 10.3390/ijms23115918. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35682601 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoexpression Patterns of Megalin, Cubilin, Caveolin-1, Gipc1 and Dab2IP in the Embryonic and Postnatal Development of the Kidneys in Yotari (Dab1-/-) Mice.Biomedicines. 2024 Jul 11;12(7):1542. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071542. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39062115 Free PMC article.
-
Connexin Expression Is Altered in the Eye Development of Yotari Mice: A Preliminary Study.Biomolecules. 2024 Sep 19;14(9):1174. doi: 10.3390/biom14091174. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39334940 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Johnson Chacko L., Wertjanz D., Sergi C., Dudas J., Fischer N., Eberharter T., Hoermann R., Glueckert R., Fritsch H., Rask-Andersen H., et al. Growth and cellular patterning during fetal human inner ear development studied by a correlative imaging approach. BMC Dev. Biol. 2019;19:11. doi: 10.1186/s12861-019-0191-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tafra R., Brakus S.M., Vukojevic K., Kablar B., Colovic Z., Saraga-Babic M. Interplay of proliferation and proapoptotic and antiapoptotic factors is revealed in the early human inner ear development. Otol. Neurotol. Off. Publ. Am. Otol. Soc. Am. Neurotol. Soc. Eur. Acad. Otol. Neurotol. 2014;35:695–703. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000000210. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

