Checkpoint Inhibitors and Induction of Celiac Disease-like Condition
- PMID: 35327411
- PMCID: PMC8945786
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10030609
Checkpoint Inhibitors and Induction of Celiac Disease-like Condition
Abstract
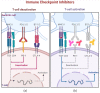
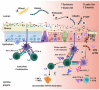
Immune checkpoint inhibitors herald a new era in oncological therapy-resistant cancer, thus bringing hope for better outcomes and quality of life for patients. However, as with other medications, they are not without serious side effects over time. Despite this, their advantages outweigh their disadvantages. Understanding the adverse effects will help therapists locate, apprehend, treat, and perhaps diminish them. The major ones are termed immune-related adverse events (irAEs), representing their auto-immunogenic capacity. This narrative review concentrates on the immune checkpoint inhibitors induced celiac disease (CD), highlighting the importance of the costimulatory inhibitors in CD evolvement and suggesting several mechanisms for CD induction. Unraveling those cross-talks and pathways might reveal some new therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: CLTA-4; Ipilimumab; Nivolumab; PD-1; celiac disease; gut toxicity; immune checkpoint inhibitor; immune toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neurologic Serious Adverse Events Associated with Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab or Nivolumab Alone in Advanced Melanoma, Including a Case Series of Encephalitis.Oncologist. 2017 Jun;22(6):709-718. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2016-0487. Epub 2017 May 11. Oncologist. 2017. PMID: 28495807 Free PMC article.
-
Patterns of toxicity burden for FDA-approved immune checkpoint inhibitors in the United States.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Jan 5;42(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02568-y. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 36600271 Free PMC article.
-
Case Report: Fulminant Celiac Disease With Combination Immune Checkpoint Therapy.Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 14;13:871452. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.871452. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35493494 Free PMC article.
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated ophthalmic adverse events: current understanding of its mechanisms, diagnosis, and management.Int J Ophthalmol. 2022 Apr 18;15(4):646-656. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2022.04.19. eCollection 2022. Int J Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35450191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of Adverse Events Following Treatment With Anti-Programmed Death-1 Agents.Oncologist. 2016 Oct;21(10):1230-1240. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2016-0055. Epub 2016 Jul 8. Oncologist. 2016. PMID: 27401894 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immune-Related Uncommon Adverse Events in Patients with Cancer Treated with Immunotherapy.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Aug 29;12(9):2091. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12092091. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36140493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The new progress in cancer immunotherapy.Clin Exp Med. 2023 Jul;23(3):553-567. doi: 10.1007/s10238-022-00887-0. Epub 2022 Sep 15. Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 36109471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cross-reactivity and sequence similarity between microbial transglutaminase and human tissue antigens.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 16;13(1):17526. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-44452-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37845267 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ben Zvi C., Ehrenfeld M., Shoenfeld Y. IMMUNOTHERAPY WITH CHECKPOINT INHIBITORS (ICPI) AND IMMUNE RELATED ADVERSE EVENTS (IRAE’S) Harefuah. 2020;159:508–515. - PubMed
-
- Hannah D. James P Allison and Tasuku Honjo Win Nobel Prize for Medicine | Nobel Prizes | The Guardian. [(accessed on 2 February 2022)]. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/science/2018/oct/01/james-p-allison-and-tasu....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

