Checkpoint Inhibitors and Induction of Celiac Disease-like Condition
- PMID: 35327411
- PMCID: PMC8945786
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10030609
Checkpoint Inhibitors and Induction of Celiac Disease-like Condition
Abstract
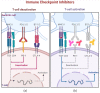
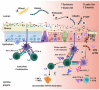
Immune checkpoint inhibitors herald a new era in oncological therapy-resistant cancer, thus bringing hope for better outcomes and quality of life for patients. However, as with other medications, they are not without serious side effects over time. Despite this, their advantages outweigh their disadvantages. Understanding the adverse effects will help therapists locate, apprehend, treat, and perhaps diminish them. The major ones are termed immune-related adverse events (irAEs), representing their auto-immunogenic capacity. This narrative review concentrates on the immune checkpoint inhibitors induced celiac disease (CD), highlighting the importance of the costimulatory inhibitors in CD evolvement and suggesting several mechanisms for CD induction. Unraveling those cross-talks and pathways might reveal some new therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: CLTA-4; Ipilimumab; Nivolumab; PD-1; celiac disease; gut toxicity; immune checkpoint inhibitor; immune toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ben Zvi C., Ehrenfeld M., Shoenfeld Y. IMMUNOTHERAPY WITH CHECKPOINT INHIBITORS (ICPI) AND IMMUNE RELATED ADVERSE EVENTS (IRAE’S) Harefuah. 2020;159:508–515. - PubMed
-
- Hannah D. James P Allison and Tasuku Honjo Win Nobel Prize for Medicine | Nobel Prizes | The Guardian. [(accessed on 2 February 2022)]. Available online: https://www.theguardian.com/science/2018/oct/01/james-p-allison-and-tasu....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

