Neural Network-Based Calculator for Rat Glomerular Filtration Rate
- PMID: 35327412
- PMCID: PMC8945373
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10030610
Neural Network-Based Calculator for Rat Glomerular Filtration Rate
Abstract
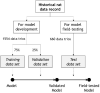
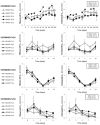
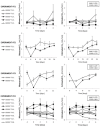
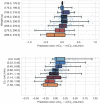
Glomerular filtration is a pivotal process of renal physiology, and its alterations are a central pathological event in acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease. Creatinine clearance (ClCr), a standard method for glomerular filtration rate (GFR) measurement, requires a long and tedious procedure of timed (usually 24 h) urine collection. We have developed a neural network (NN)-based calculator of rat ClCr from plasma creatinine (pCr) and body weight. For this purpose, matched pCr, weight, and ClCr trios from our historical records on male Wistar rats were used. When evaluated on the training (1165 trios), validation (389), and test sets (660), the model committed an average prediction error of 0.196, 0.178, and 0.203 mL/min and had a correlation coefficient of 0.863, 0.902, and 0.856, respectively. More importantly, for all datasets, the NN seemed especially effective at comparing ClCr among groups within individual experiments, providing results that were often more congruent than those measured experimentally. ACLARA, a friendly interface for this calculator, has been made publicly available to ease and expedite experimental procedures and to enhance animal welfare in alignment with the 3Rs principles by avoiding unnecessary stressing metabolic caging for individual urine collection.
Keywords: calculator; creatinine clearance; machine learning; neural network; rat glomerular filtration rate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

