Predictive Value of Urinary Aquaporin 2 for Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Acute Decompensated Heart Failure
- PMID: 35327416
- PMCID: PMC8945460
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10030613
Predictive Value of Urinary Aquaporin 2 for Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Acute Decompensated Heart Failure
Abstract
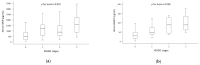
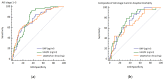
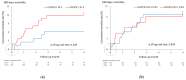
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is frequently encountered in people with acute decompensated heart failure (ADHF) and is associated with increased morbidity and mortality. Early detection of a urinary biomarker of kidney injury might allow a prompt diagnosis and improve outcomes. Levels of urinary aquaporin 2 (UAQP2), which is also associated with several renal diseases, are increased with ADHF. We aimed to determine whether UAQP2 predicted AKI in patients with ADHF. We conducted a prospective observation study in the coronary care unit (CCU) in a tertiary care university hospital in Taiwan. Individuals with ADHF admitted to the CCU between November 2009 and November 2014 were enrolled, and serum and urinary samples were collected. AKI was diagnosed in 69 (36.5%) of 189 adult patients (mean age: 68 years). Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) of biomarkers was evaluated to evaluate the diagnostic power for AKI. Both brain natriuretic peptide and UAQP2 demonstrated acceptable AUROCs (0.759 and 0.795, respectively). A combination of the markers had an AUROC of 0.802. UAQP2 is a potential biomarker of AKI in CCU patients with ADHF. Additional research on this novel biomarker is required.
Keywords: acute decompensated heart failure; acute kidney injury; coronary care unit; urinary aquaporin 2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combination of Urinary Biomarkers Improves Early Detection of Acute Kidney Injury in Patients With Heart Failure.Circ J. 2016;80(4):1017-23. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-15-0886. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Circ J. 2016. PMID: 26888148
-
Novel urinary biomarkers in detecting acute kidney injury, persistent renal impairment, and all-cause mortality following decongestive therapy in acute decompensated heart failure.J Card Fail. 2013 Sep;19(9):621-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2013.07.004. J Card Fail. 2013. PMID: 24054338 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma thrombomodulin levels are associated with acute kidney injury in patients with acute heart failure.Ann Med. 2022 Dec;54(1):3169-3176. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2142660. Ann Med. 2022. PMID: 36354140 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging microRNA biomarkers for acute kidney injury in acute decompensated heart failure.Heart Fail Rev. 2021 Sep;26(5):1203-1217. doi: 10.1007/s10741-020-09928-w. Heart Fail Rev. 2021. PMID: 32062825 Review.
-
Sodium-based osmotherapy for hyponatremia in acute decompensated heart failure.Heart Fail Rev. 2022 Mar;27(2):379-391. doi: 10.1007/s10741-021-10124-7. Epub 2021 Nov 12. Heart Fail Rev. 2022. PMID: 34767112 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring Aquaporins in Human Studies: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential in Critical Illness.Life (Basel). 2024 Dec 20;14(12):1688. doi: 10.3390/life14121688. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39768394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Urinary Extracellular Vesicles for Non-Invasive Quantification of Principal Cell Damage in Kidney Transplant Recipients.Biomolecules. 2024 Sep 5;14(9):1124. doi: 10.3390/biom14091124. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39334890 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Heywood J.T., Fonarow G.C., Costanzo M.R., Mathur V.S., Wigneswaran J.R., Wynne J., Committee A.S.A. Investigators. High prevalence of renal dysfunction and its impact on outcome in 118,465 patients hospitalized with acute decompensated heart failure: A report from the ADHERE database. J. Card. Fail. 2007;13:422–430. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2007.03.011. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ostermann M., Zarbock A., Goldstein S., Kashani K., Macedo E., Murugan R., Bell M., Forni L., Guzzi L., Joannidis M., et al. Recommendations on Acute Kidney Injury Biomarkers From the Acute Disease Quality Initiative Consensus Conference: A Consensus Statement. JAMA Netw. Open. 2020;3:e2019209. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19209. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

