Bezafibrate Reduces Elevated Hepatic Fumarate in Insulin-Deficient Mice
- PMID: 35327418
- PMCID: PMC8945094
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10030616
Bezafibrate Reduces Elevated Hepatic Fumarate in Insulin-Deficient Mice
Abstract
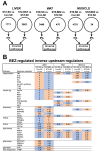
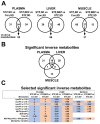
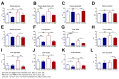
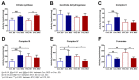
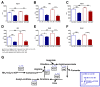
Glucotoxic metabolites and pathways play a crucial role in diabetic complications, and new treatment options which improve glucotoxicity are highly warranted. In this study, we analyzed bezafibrate (BEZ) treated, streptozotocin (STZ) injected mice, which showed an improved glucose metabolism compared to untreated STZ animals. In order to identify key molecules and pathways which participate in the beneficial effects of BEZ, we studied plasma, skeletal muscle, white adipose tissue (WAT) and liver samples using non-targeted metabolomics (NMR spectroscopy), targeted metabolomics (mass spectrometry), microarrays and mitochondrial enzyme activity measurements, with a particular focus on the liver. The analysis of muscle and WAT demonstrated that STZ treatment elevated inflammatory pathways and reduced insulin signaling and lipid pathways, whereas BEZ decreased inflammatory pathways and increased insulin signaling and lipid pathways, which can partly explain the beneficial effects of BEZ on glucose metabolism. Furthermore, lysophosphatidylcholine levels were lower in the liver and skeletal muscle of STZ mice, which were reverted in BEZ-treated animals. BEZ also improved circulating and hepatic glucose levels as well as lipid profiles. In the liver, BEZ treatment reduced elevated fumarate levels in STZ mice, which was probably due to a decreased expression of urea cycle genes. Since fumarate has been shown to participate in glucotoxic pathways, our data suggests that BEZ treatment attenuates the urea cycle in the liver, decreases fumarate levels and, in turn, ameliorates glucotoxicity and reduces insulin resistance in STZ mice.
Keywords: bezafibrate; diabetes; fumarate; insulin resistance; lysophosphatidylcholine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. A.F. is an employee of JOTEC GmbH, however, the company had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

