Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Responses of Alveolar Epithelial Cells: Implications for COVID-19 Lung Pathology
- PMID: 35327420
- PMCID: PMC8945544
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10030618
Immune-Mediated Inflammatory Responses of Alveolar Epithelial Cells: Implications for COVID-19 Lung Pathology
Abstract
Background: Clinical and experimental evidence point to a dysregulated immune response caused by SARS-CoV-2 as the primary mechanism of lung disease in COVID-19. However, the pathogenic mechanisms underlying COVID-19-associated ARDS (Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome) remain incompletely understood. This study aims to explore the inflammatory responses of alveolar epithelial cells to either the spike S1 protein or to a mixture of cytokines secreted by S1-activated macrophages.
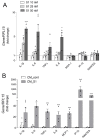
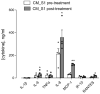
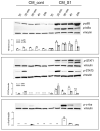
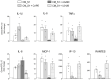
Methods and results: The exposure of alveolar A549 cells to supernatants from spike-activated macrophages caused a further release of inflammatory mediators, with IL-8 reaching massive concentrations. The investigation of the molecular pathways indicated that NF-kB is involved in the transcription of IP-10 and RANTES, while STATs drive the expression of all the cytokines/chemokines tested, with the exception of IL-8 which is regulated by AP-1. Cytokines/chemokines produced by spike-activated macrophages are also likely responsible for the observed dysfunction of barrier integrity in Human Alveolar Epithelial Lentivirus-immortalized cells (hAELVi), as demonstrated by an increased permeability of the monolayers to mannitol, a marked decrease of TEER and a disorganization of claudin-7 distribution.
Conclusion: Upon exposure to supernatants from S1-activated macrophages, A549 cells act both as targets and sources of cytokines/chemokines, suggesting that alveolar epithelium along with activated macrophages may orchestrate lung inflammation and contribute to alveolar injury, a hallmark of ARDS.
Keywords: COVID-19; IL-8; chemokines; cytokines; epithelial barrier dysfunction; human alveolar epithelial cells; human macrophages.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modulating the Barrier Function of Human Alveolar Epithelial (hAELVi) Cell Monolayers as a Model of Inflammation.Altern Lab Anim. 2020 Sep-Nov;48(5-6):252-267. doi: 10.1177/0261192920983015. Epub 2021 Jan 29. Altern Lab Anim. 2020. PMID: 33513307
-
Growth Arrest of Alveolar Cells in Response to Cytokines from Spike S1-Activated Macrophages: Role of IFN-γ.Biomedicines. 2022 Dec 1;10(12):3085. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10123085. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36551841 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine-Induced iNOS in A549 Alveolar Epithelial Cells: A Potential Role in COVID-19 Lung Pathology.Biomedicines. 2023 Oct 3;11(10):2699. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11102699. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37893073 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Macrophages and Alveolar Epithelial Cells in the Development of ARDS.Inflammation. 2023 Feb;46(1):47-55. doi: 10.1007/s10753-022-01726-w. Epub 2022 Sep 1. Inflammation. 2023. PMID: 36048270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunohistochemical detection of sepsis-induced lung injury in human autopsy material.Leg Med (Tokyo). 2003 Jun;5(2):73-86. doi: 10.1016/s1344-6223(03)00010-5. Leg Med (Tokyo). 2003. PMID: 12935535 Review.
Cited by
-
Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Spike Protein S1 Induces Methylglyoxal-Derived Hydroimidazolone/Receptor for Advanced Glycation End Products (MG-H1/RAGE) Activation to Promote Inflammation in Human Bronchial BEAS-2B Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 3;24(19):14868. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914868. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834316 Free PMC article.
-
The SARS-CoV-2 S1 Spike Protein Promotes MAPK and NF-kB Activation in Human Lung Cells and Inflammatory Cytokine Production in Human Lung and Intestinal Epithelial Cells.Microorganisms. 2022 Oct 10;10(10):1996. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10101996. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36296272 Free PMC article.
-
Luteolin-rich fraction from Perilla frutescens seed meal inhibits spike glycoprotein S1 of SARS-CoV-2-induced NLRP3 inflammasome lung cell inflammation via regulation of JAK1/STAT3 pathway: A potential anti-inflammatory compound against inflammation-induced long-COVID.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 9;9:1072056. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1072056. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36698809 Free PMC article.
-
Hesperetin from Root Extract of Clerodendrum petasites S. Moore Inhibits SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 Subunit-Induced NLRP3 Inflammasome in A549 Lung Cells via Modulation of the Akt/MAPK/AP-1 Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 7;23(18):10346. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810346. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142258 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen Sulfide Ameliorates SARS-CoV-2-Associated Lung Endothelial Barrier Disruption.Biomedicines. 2023 Jun 22;11(7):1790. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11071790. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37509430 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

