Hypouricemia and Urate Transporters
- PMID: 35327453
- PMCID: PMC8945357
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10030652
Hypouricemia and Urate Transporters
Abstract
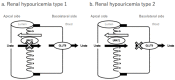
Hypouricemia is recognized as a rare disorder, defined as a serum uric acid level of 2.0 mg/dL or less. Hypouricemia is divided into an overexcretion type and an underproduction type. The former typical disease is xanthinuria, and the latter is renal hypouricemia (RHUC). The frequency of nephrogenic hypouricemia due to a deficiency of URAT1 is high in Japan, accounting for most asymptomatic and persistent cases of hypouricemia. RHUC results in a high risk of exercise-induced acute kidney injury and urolithiasis. It is vital to promote research on RHUC, as this will lead not only to the elucidation of its pathophysiology but also to the development of new treatments for gout and hyperuricemia.
Keywords: URAT1; hypouricemia; renal hypouricemia; urate transporter; xanthinuria.
Conflict of interest statement
N.O., M.O., K.M. and N.A. declare no conflicts of interest. I.H. reports receiving a lecturer’s fee from Mochida Pharmaceutical Company, Sanwa Kagaku Kenkyusho Co., Ltd., Teijin Pharma Co., Lyd., and Fuji Yakuhin Co., Ltd., and research grants from Mochida Pharmaceutical Company, Teijin Pharma, Fuji Yakuhin Co., Ltd., and Sanwa Kagaku Kenkyusho Co., Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Japanese Society of Gout and Nucleic Acid Metabolism . Japanese Guideline for the Management of Hyperuricemia and Gout. 3rd ed. Shindan To Chiryo Sha, Inc.; Tokyo, Japan: 2018. pp. 18–23.
-
- Johnson R.J., Kang D.H., Feig D., Kivlighn S., Kanellis J., Watanabe S., Tuttle K.R., Rodriguez-Iturbe B., Herrera-Acosta J., Mazzali M. Is there a pathogenetic role for uric acid in hypertension and cardiovascular and renal disease? Hypertension. 2003;41:1183–1190. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.0000069700.62727.C5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kikuchi Y., Koga H., Yasutomo Y., Kawabata Y., Shimizu E., Naruse M., Kiyama S., Nonoguchi H., Tomita K., Sasatomi Y., et al. Patients with renal hypouricemia with exercise-induced acute renal failure and chronic renal dysfunction. Clin. Nephrol. 2000;53:467–472. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

