The Pyrazolo[3,4- d]Pyrimidine Derivative Si306 Encapsulated into Anti-GD2-Immunoliposomes as Therapeutic Treatment of Neuroblastoma
- PMID: 35327462
- PMCID: PMC8945814
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10030659
The Pyrazolo[3,4- d]Pyrimidine Derivative Si306 Encapsulated into Anti-GD2-Immunoliposomes as Therapeutic Treatment of Neuroblastoma
Abstract
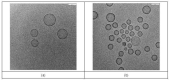
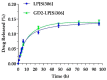
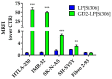
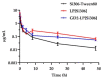
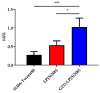
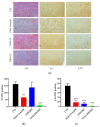
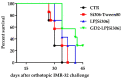
Si306, a pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidine derivative recently identified as promising anticancer agent, has shown favorable in vitro and in vivo activity profile against neuroblastoma (NB) models by acting as a competitive inhibitor of c-Src tyrosine kinase. Nevertheless, Si306 antitumor activity is associated with sub-optimal aqueous solubility, which might hinder its further development. Drug delivery systems were here developed with the aim to overcome this limitation, obtaining suitable formulations for more efficacious in vivo use. Si306 was encapsulated in pegylated stealth liposomes, undecorated or decorated with a monoclonal antibody able to specifically recognize and bind to the disialoganglioside GD2 expressed by NB cells (LP[Si306] and GD2-LP[Si306], respectively). Both liposomes possessed excellent morphological and physio-chemical properties, maintained over a period of two weeks. Compared to LP[Si306], GD2-LP[Si306] showed in vitro specific cellular targeting and increased cytotoxic activity against NB cell lines. After intravenous injection in healthy mice, pharmacokinetic profiles showed increased plasma exposure of Si306 when delivered by both liposomal formulations, compared to that obtained when Si306 was administered as free form. In vivo tumor homing and cytotoxic effectiveness of both liposomal formulations were finally tested in an orthotopic animal model of NB. Si306 tumor uptake resulted significantly higher when encapsulated in GD2-LP, compared to Si306, either free or encapsulated into untargeted LP. This, in turn, led to a significant increase in survival of mice treated with GD2-LP[Si306]. These results demonstrate a promising antitumor efficacy of Si306 encapsulated into GD2-targeted liposomes, supporting further therapeutic developments in pre-clinical trials and in the clinic for NB.
Keywords: anti-GD2 monoclonal antibody; c-Src inhibitor; immunoliposomes; liposomes; neuroblastoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
In vitro and in vivo antitumor activity of liposomal Fenretinide targeted to human neuroblastoma.Int J Cancer. 2003 May 1;104(5):559-67. doi: 10.1002/ijc.10991. Int J Cancer. 2003. PMID: 12594810
-
Anti-GD2 Immunoliposomes for Targeted Delivery of the Survivin Inhibitor Sepantronium Bromide (YM155) to Neuroblastoma Tumor Cells.Pharm Res. 2018 Mar 7;35(4):85. doi: 10.1007/s11095-018-2373-x. Pharm Res. 2018. PMID: 29516187 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoliposomal fenretinide: a novel antitumoral drug for human neuroblastoma.Cancer Lett. 2003 Jul 18;197(1-2):151-5. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3835(03)00097-1. Cancer Lett. 2003. PMID: 12880975 Review.
-
Doxorubicin-loaded Fab' fragments of anti-disialoganglioside immunoliposomes selectively inhibit the growth and dissemination of human neuroblastoma in nude mice.Cancer Res. 2003 Jan 1;63(1):86-92. Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 12517782
-
Immunoliposomes for Neuroblastoma: Review of the Past Experience and Design of a Novel Nanoparticle.Anticancer Res. 2024 Nov;44(11):4665-4675. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.17294. Anticancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39477321 Review.
Cited by
-
Editorial of the Special Issue "Targeted Therapies for Cancer".Biomedicines. 2022 May 11;10(5):1114. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10051114. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35625850 Free PMC article.
-
Small Molecule Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors (TKIs) for Glioblastoma Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 23;25(3):1398. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031398. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
One-Pot Synthesis of Novel Pyrimidine Derivatives with Potential Antidiabetic Activity Through Dual α-Glucosidase and α-Amylase Inhibitors.Molecules. 2025 Jul 4;30(13):2857. doi: 10.3390/molecules30132857. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40649371 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

