Gene Variants Involved in Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay Suggest a Role in Autism Spectrum Disorder
- PMID: 35327467
- PMCID: PMC8945030
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10030665
Gene Variants Involved in Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay Suggest a Role in Autism Spectrum Disorder
Abstract
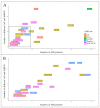
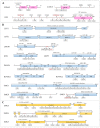
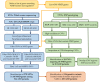
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a heterogeneous neurodevelopmental condition with unclear etiology. Many genes have been associated with ASD risk, but the underlying mechanisms are still poorly understood. An important post-transcriptional regulatory mechanism that plays an essential role during neurodevelopment, the Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay (NMD) pathway, may contribute to ASD risk. In this study, we gathered a list of 46 NMD factors and regulators and investigated the role of genetic variants in these genes in ASD. By conducting a comprehensive search for Single Nucleotide Variants (SNVs) in NMD genes using Whole Exome Sequencing data from 1828 ASD patients, we identified 270 SNVs predicted to be damaging in 28.7% of the population. We also analyzed Copy Number Variants (CNVs) from two cohorts of ASD patients (N = 3570) and discovered 38 CNVs in 1% of cases. Importantly, we discovered 136 genetic variants (125 SNVs and 11 CNVs) in 258 ASD patients that were located within protein domains required for NMD. These gene variants are classified as damaging using in silico prediction tools, and therefore may interfere with proper NMD function in ASD. The discovery of NMD genes as candidates for ASD in large patient genomic datasets provides evidence supporting the involvement of the NMD pathway in ASD pathophysiology.
Keywords: autism spectrum disorder; copy number variants; nonsense-mediated mRNA decay; single nucleotide variants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Role for Gene-Environment Interactions in Autism Spectrum Disorder Is Supported by Variants in Genes Regulating the Effects of Exposure to Xenobiotics.Front Neurosci. 2022 May 19;16:862315. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.862315. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35663546 Free PMC article.
-
An integrated analysis of rare CNV and exome variation in Autism Spectrum Disorder using the Infinium PsychArray.Sci Rep. 2020 Feb 21;10(1):3198. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-59922-3. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32081867 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic architecture of autism spectrum disorder in Qatar: The BARAKA-Qatar Study.Genome Med. 2023 Oct 7;15(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s13073-023-01228-w. Genome Med. 2023. PMID: 37805537 Free PMC article.
-
Childhood-Onset Schizophrenia: A Systematic Overview of Its Genetic Heterogeneity From Classical Studies to the Genomic Era.Front Genet. 2019 Dec 18;10:1137. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.01137. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31921276 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic architecture of autism spectrum disorder: Lessons from large-scale genomic studies.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021 Sep;128:244-257. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.06.028. Epub 2021 Jun 21. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021. PMID: 34166716 Review.
Cited by
-
mRNA Metabolism in Health and Disease.Biomedicines. 2022 Sep 13;10(9):2262. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10092262. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36140363 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic ablation of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 in rats results in an autism-like behavioral phenotype.PLoS One. 2022 Nov 16;17(11):e0275937. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0275937. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36383609 Free PMC article.
-
Direct and indirect effects of spliceosome disruption compromise gene regulation by Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Dec 27:2024.12.27.630533. doi: 10.1101/2024.12.27.630533. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39763844 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Spatial expression of the nonsense-mediated mRNA decay factors UPF3A and UPF3B among mouse tissues.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2023 Nov 15;24(11):1062-1068. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B2300126. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2023. PMID: 37961809 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel UPF1 Variant Associated With a Rare UPF1-Related Neurodevelopmental Disorder.Clin Genet. 2025 Feb 24;108(3):313-7. doi: 10.1111/cge.14735. Online ahead of print. Clin Genet. 2025. PMID: 39993774 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th ed. Am. Psychiatr. Publ.; Washington, DC, USA: 2013.
-
- Sanders S., Ercan-sencicek G., Hus V., Luo R., Murtha M.T., Moreno-De-Luca D., State M. Multiple recurrent de novo copy number variations (CNVs), including duplications of the 7q11.23 Williams-Beuren syndrome region, are strongly associated with autism. Neuron. 2011;70:863–885. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.05.002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- PAC-POCI-01-0145-FEDER-016428/Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia
- PD/BD/113773/2015/Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia
- PD/BD/114386/2016/Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia
- UIDB/04046/2020 and UIDP/04046/2020/Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia
- PD/BD/131390/2017/Fundação para a Ciência e Tecnologia
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

