Epithelial-Fibroblast Crosstalk Protects against Acidosis-Induced Inflammatory and Fibrotic Alterations
- PMID: 35327483
- PMCID: PMC8945333
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10030681
Epithelial-Fibroblast Crosstalk Protects against Acidosis-Induced Inflammatory and Fibrotic Alterations
Abstract
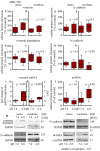
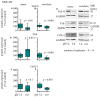
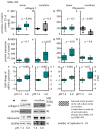
Pathogenesis of chronic kidney disease (CKD) is accompanied by extracellular acidosis inflammation, fibrosis and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). The aim of this study was to assess the influence of acidosis on tubule epithelial cells (NRK-52E) and fibroblasts (NRK-49F) in dependence of cellular crosstalk. NRK-52E and NRK-49F were used in mono- and co-cultures, and were treated with acidic media (pH 6.0) for 48 h. The intracellular proteins were measured by Western blot. Secreted proteins were measured by ELISA. Distribution of E-cadherin was assessed by immunofluorescence and epithelial barrier function by FITC-dextran diffusion. Inflammation: Acidosis led to an increase in COX-2 in NRK-52E and TNF in NRK-49F in monoculture. In co-culture, this effect was reversed. EMT: Acidosis led to an increase in vimentin protein in both cell lines, whereas in co-culture, the effect was abolished. In NRK-52E, the E-cadherin expression was unchanged, but subcellular E-cadherin showed a disturbed distribution, and cellular barrier function was decreased. Fibrosis: Monoculture acidosis led to an increased secretion of collagen I and fibronectin in NRK-52E and collagen I in NRK-49F. In co-culture, the total collagen I secretion was unchanged, and fibronectin secretion was decreased. Intercellular crosstalk between epithelial cells and fibroblasts has a protective function regarding the development of acidosis-induced damage.
Keywords: EMT; cellular crosstalk; chronic kidney diseases; extracellular acidosis; fibrosis; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare to have no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Crosstalk with renal proximal tubule cells drives acidosis-induced inflammatory response and dedifferentiation of fibroblasts via p38-singaling.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Feb 24;22(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01527-8. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38395872 Free PMC article.
-
Acidosis Activates the Nrf2 Pathway in Renal Proximal Tubule-Derived Cells through a Crosstalk with Renal Fibroblasts.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Feb 8;12(2):412. doi: 10.3390/antiox12020412. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829971 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial-fibroblast cross talk aggravates the impact of the nephrotoxin ochratoxin A.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019 Dec;1866(12):118528. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2019.118528. Epub 2019 Aug 12. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2019. PMID: 31415839
-
Novel RAS inhibitor 25-O-methylalisol F attenuates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and tubulo-interstitial fibrosis by selectively inhibiting TGF-β-mediated Smad3 phosphorylation.Phytomedicine. 2018 Mar 15;42:207-218. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.03.034. Epub 2018 Mar 19. Phytomedicine. 2018. PMID: 29655688
-
Beta-casomorphin-7 prevents epithelial-mesenchymal transdifferentiation of NRK-52E cells at high glucose level: Involvement of AngII-TGF-β1 pathway.Peptides. 2015 Aug;70:37-44. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2015.04.002. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Peptides. 2015. PMID: 25882007
Cited by
-
Crosstalk with renal proximal tubule cells drives acidosis-induced inflammatory response and dedifferentiation of fibroblasts via p38-singaling.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Feb 24;22(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01527-8. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38395872 Free PMC article.
-
Carbonic anhydrase IX promotes acute lung injury and mortality in females during metabolic acidosis and pneumonia.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2025 Aug 1;329(2):L266-L281. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00331.2024. Epub 2025 Jul 7. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40623021 Free PMC article.
-
Hypothesis-generating analysis of the impact of non-damaging metabolic acidosis on the transcriptome of different cell types: Integrated stress response (ISR) modulation as general transcriptomic reaction to non-respiratory acidic stress?PLoS One. 2023 Aug 25;18(8):e0290373. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0290373. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37624790 Free PMC article.
-
Gastrodin attenuates renal injury and collagen deposition via suppression of the TGF-β1/Smad2/3 signaling pathway based on network pharmacology analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 17;14:1082281. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1082281. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36733505 Free PMC article.
-
Acidosis Activates the Nrf2 Pathway in Renal Proximal Tubule-Derived Cells through a Crosstalk with Renal Fibroblasts.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Feb 8;12(2):412. doi: 10.3390/antiox12020412. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829971 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

