Targeting CDK4/6 for Anticancer Therapy
- PMID: 35327487
- PMCID: PMC8945444
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10030685
Targeting CDK4/6 for Anticancer Therapy
Abstract
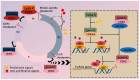
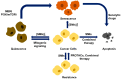
Cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 (CDK4/6) are key regulators of the cell cycle and are deemed as critical therapeutic targets of multiple cancers. Various approaches have been applied to silence CDK4/6 at different levels, i.e., CRISPR to knock out at the DNA level, siRNA to inhibit translation, and drugs that target the protein of interest. Here we summarize the current status in this field, highlighting the mechanisms of small molecular inhibitors treatment and drug resistance. We describe approaches to combat drug resistance, including combination therapy and PROTACs drugs that degrade the kinases. Finally, critical issues and perspectives in the field are outlined.
Keywords: CDK4/6; PROTAC; abemaciclib; cancer; drug resistance; palbociclib; ribociclib; small molecular inhibitor; trilaciclib.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Clinical Management of Potential Toxicities and Drug Interactions Related to Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibitors in Breast Cancer: Practical Considerations and Recommendations.Oncologist. 2017 Sep;22(9):1039-1048. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2017-0142. Epub 2017 Jul 13. Oncologist. 2017. PMID: 28706010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differences in metabolic transport and resistance mechanisms of Abemaciclib, Palbociclib, and Ribociclib.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jul 5;14:1212986. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1212986. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37475713 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A unique CDK4/6 inhibitor: Current and future therapeutic strategies of abemaciclib.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Jun;156:104686. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104686. Epub 2020 Feb 14. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32068118 Review.
-
Cyclin-dependent protein kinase inhibitors including palbociclib as anticancer drugs.Pharmacol Res. 2016 May;107:249-275. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.03.012. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 26995305 Review.
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer: palbociclib, ribociclib, and abemaciclib.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2017 Nov;166(1):41-54. doi: 10.1007/s10549-017-4385-3. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2017. PMID: 28741274 Review.
Cited by
-
The Potential Revolution of Cancer Treatment with CRISPR Technology.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Mar 17;15(6):1813. doi: 10.3390/cancers15061813. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36980699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TFAP2C-DDR1 axis regulates resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitor in breast cancer.Cancer Lett. 2025 Feb 1;610:217356. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2024.217356. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Cancer Lett. 2025. PMID: 39603379
-
A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study of Basophil Count and Risk of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus.Int J Womens Health. 2025 Feb 26;17:517-527. doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S500632. eCollection 2025. Int J Womens Health. 2025. PMID: 40028461 Free PMC article.
-
CDK4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer therapy: mechanisms of drug resistance and strategies for treatment.Front Pharmacol. 2025 May 12;16:1549520. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1549520. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40421216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The landscape of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitors in solid malignancies: emphasis on immunotherapy combinatorial strategies.Med Oncol. 2025 Aug 26;42(10):447. doi: 10.1007/s12032-025-02996-8. Med Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40856900 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

