Elevated Pre-Treatment Serum MMP-7 Levels Are Associated with the Presence of Metastasis and Poor Survival in Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma
- PMID: 35327500
- PMCID: PMC8945654
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10030698
Elevated Pre-Treatment Serum MMP-7 Levels Are Associated with the Presence of Metastasis and Poor Survival in Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma
Abstract
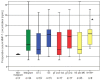
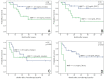
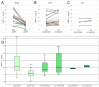
Upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC) is a rare cancer with a barely predictable clinical behaviour. Serum MMP-7 is a validated prognostic marker in urothelial bladder cancer, a tumour entity with large clinical, histological, and molecular similarity to UTUC. The serum MMP-7 levels have not yet been investigated in UTUC. In the present study, we determined MMP-7 concentrations in an overall number of 103 serum samples from 57 UTUC patients who underwent surgical or systemic (platinum or immune checkpoint inhibitor) therapy by using the ELISA method. In addition to pre-treatment samples, the serum samples collected at predefined time points after or during therapy were also investigated. Serum MMP-7 concentrations were correlated with clinicopathological and follow-up data. Our results revealed significantly, two-fold elevated pre-treatment serum MMP-7 levels in metastatic cases of UTUC in both the radical surgery- and the chemotherapy-treated cohorts (p = 0.045 and p = 0.040, respectively). In addition, high serum MMP-7 levels significantly decreased after radical surgery, and high pre-treatment MMP-7 concentrations were associated with shorter survival both in the surgery- and chemotherapy-treated cohorts (p = 0.029 and p = 0.001, respectively). Our results revealed pre-treatment serum MMP-7 as a prognostic marker for UTUC, which may help to improve preoperative risk-stratification and thereby improve therapeutic decision-making.
Keywords: MMP-7; UTUC; biomarker; chemotherapy; immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy; matrix metalloproteinase; prognosis; radical nephroureterectomy; upper urinary tract cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Boris Hadaschik reported personal fees and non-financial support from AstraZeneca, Amgen, Bayer, BMS, and Janssen; personal fees from ABX, Lightpoint medical Inc, and Pfizer; and grant funding from German Research Foundation, BMS, and Novartis, all outside the submitted work. Tibor Szarvas received fees from BRAHMS and Janssen outside of the present study. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High Pretreatment Serum PD-L1 Levels Are Associated with Muscle Invasion and Shorter Survival in Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma.Biomedicines. 2022 Oct 13;10(10):2560. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102560. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36289821 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of plasma fibrinogen levels in patients with localized upper tract urothelial carcinoma.BJU Int. 2013 May;111(6):857-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11353.x. Epub 2012 Jul 3. BJU Int. 2013. PMID: 22757942
-
C-reactive protein: a biomarker of survival in patients with localized upper tract urothelial carcinoma treated with radical nephroureterectomy.Urol Oncol. 2013 Nov;31(8):1725-30. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2012.05.008. Epub 2012 Nov 8. Urol Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23141922
-
Prognostic value of preoperative lymphocyte-related systemic inflammatory biomarkers in upper tract urothelial carcinoma patients treated with radical nephroureterectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.World J Surg Oncol. 2020 Oct 23;18(1):273. doi: 10.1186/s12957-020-02048-7. World J Surg Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33097052 Free PMC article.
-
European Association of Urology Guidelines on Upper Urinary Tract Urothelial Carcinoma: 2017 Update.Eur Urol. 2018 Jan;73(1):111-122. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.07.036. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Eur Urol. 2018. PMID: 28867446 Review.
Cited by
-
High Pretreatment Serum PD-L1 Levels Are Associated with Muscle Invasion and Shorter Survival in Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma.Biomedicines. 2022 Oct 13;10(10):2560. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10102560. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36289821 Free PMC article.
-
ANRIL promotes the regulation of colorectal cancer on lymphatic endothelial cells via VEGF-C and is the key target for Pien Tze Huang to inhibit cancer metastasis.Cancer Gene Ther. 2023 Sep;30(9):1260-1273. doi: 10.1038/s41417-023-00635-w. Epub 2023 Jun 7. Cancer Gene Ther. 2023. PMID: 37286729 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-, Tissue- and Urine-Based Prognostic Biomarkers of Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Aug 31;14(17):1927. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14171927. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive Analysis of the Prognostic Value of Circulating MMP-7 Levels in Urothelial Carcinoma: A Combined Cohort Analysis, Systematic Review, and Meta-Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 26;24(9):7859. doi: 10.3390/ijms24097859. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175566 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Soria F., Shariat S.F., Lerner S.P., Fritsche H.M., Rink M., Kassouf W., Spiess P.E., Lotan Y., Ye D., Fernández M.I., et al. Epidemiology, diagnosis, preoperative evaluation and prognostic assessment of upper-tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC) World J. Urol. 2017;35:379–387. doi: 10.1007/s00345-016-1928-x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Birtle A., Johnson M., Chester J., Jones R., Dolling D., Bryan R.T., Harris C., Winterbottom A., Blacker A., Catto J.W.F., et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy in upper tract urothelial carcinoma (the POUT trial): A phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2020;395:1268–1277. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30415-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
- 139059/National Research, Development and Innovation Office
- ÚNKP-21-5-SE-3/New National Excellence Program of the Ministry for Innovation and Technology by the National Research, Development and Innovation Fund
- BO/00451/20/5/János Bolyai Research Scholarship of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences
- 2019.118.1/Wilhelm Sander Foundation
- D/107-137709/IFORES
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

