Clinical Interest of Serum Alpha-2 Macroglobulin, Apolipoprotein A1, and Haptoglobin in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, with and without Type 2 Diabetes, before or during COVID-19
- PMID: 35327501
- PMCID: PMC8945355
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10030699
Clinical Interest of Serum Alpha-2 Macroglobulin, Apolipoprotein A1, and Haptoglobin in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, with and without Type 2 Diabetes, before or during COVID-19
Abstract
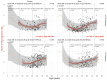
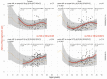
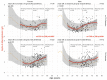
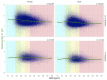
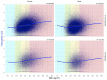
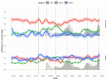
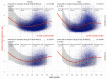
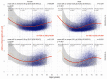
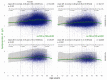
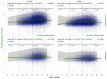
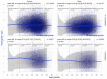
In patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) with or without type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), alpha-2 macroglobulin (A2M), apolipoprotein A1 (ApoA1), and haptoglobin are associated with the risk of liver fibrosis, inflammation (NASH), and COVID-19. We assessed if these associations were worsened by T2DM after adjustment by age, sex, obesity, and COVID-19. Three datasets were used: the “Control Population”, which enabled standardization of protein serum levels according to age and sex (N = 27,382); the “NAFLD-Biopsy” cohort for associations with liver features (N = 926); and the USA “NAFLD-Serum” cohort for protein kinetics before and during COVID-19 (N = 421,021). The impact of T2DM was assessed by comparing regression curves adjusted by age, sex, and obesity for the liver features in “NAFLD-Biopsy”, and before and during COVID-19 pandemic peaks in “NAFLD-Serum”. Patients with NAFLD without T2DM, compared with the values of controls, had increased A2M, decreased ApoA1, and increased haptoglobin serum levels. In patients with both NAFLD and T2DM, these significant mean differences were magnified, and even more during the COVID-19 pandemic in comparison with the year 2019 (all p < 0.001), with a maximum ApoA1 decrease of 0.21 g/L in women, and a maximum haptoglobin increase of 0.17 g/L in men. In conclusion, T2DM is associated with abnormal levels of A2M, ApoA1, and haptoglobin independently of NAFLD, age, sex, obesity, and COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; SAF-scoring system; alpha-2 macroglobulin; apolipoprotein A1; haptoglobin; liver fibrosis; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease NAFLD; non-alcoholic steatohepatitis NASH; steatosis; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
TP is the inventor of FibroTest (FibroSure in USA) and NASH-FibroTest, and the co-founder of BioPredictive. The patents belong to French public organizations Assistance Publique Hôpitaux de Paris and Sorbonne University. OD is cofounder BioPredictive. OD and VP are full employee of BioPredictive. The other coauthors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
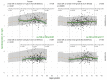
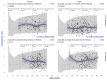
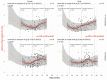
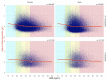
Similar articles
-
IMPACT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES ON NONALCOHOLIC STEATOHEPATITIS AND ADVANCED FIBROSIS IN PATIENTS WITH NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE.Endocr Pract. 2020 Apr;26(4):444-453. doi: 10.4158/EP-2019-0342. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Endocr Pract. 2020. PMID: 31968197
-
Histopathological differences utilizing the nonalcoholic fatty liver disease activity score criteria in diabetic (type 2 diabetes mellitus) and non-diabetic patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.World J Hepatol. 2015 Nov 8;7(25):2610-8. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i25.2610. World J Hepatol. 2015. PMID: 26557954 Free PMC article.
-
Histopathological differences in patients with biopsy-proven non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with and without type 2 diabetes.Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr (Engl Ed). 2018 Jun-Jul;65(6):354-360. doi: 10.1016/j.endinu.2017.12.011. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr (Engl Ed). 2018. PMID: 29477355 English, Spanish.
-
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Treatment in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus; New Kids on the Block.Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2020;18(2):172-181. doi: 10.2174/1570161117666190405164313. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 30961499 Review.
-
The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Hepatol. 2019 Oct;71(4):793-801. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.06.021. Epub 2019 Jul 4. J Hepatol. 2019. PMID: 31279902
Cited by
-
Diabetes: A Multifaceted Disorder.Biomedicines. 2022 Jul 14;10(7):1698. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10071698. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35885003 Free PMC article.
-
Global epidemiology of type 2 diabetes in patients with NAFLD or MAFLD: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Med. 2024 Mar 6;22(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s12916-024-03315-0. BMC Med. 2024. PMID: 38448943 Free PMC article.
-
Association of apolipoprotein A1 levels with lumbar bone mineral density and β-CTX in osteoporotic fracture individuals: a cross-sectional investigation.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Jul 31;11:1415739. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1415739. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39144661 Free PMC article.
-
[Establishment and validation of a predictive nomogram for liver fibrosis in patients with Wilson disease and abnormal lipid metabolism].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022 Nov 20;42(11):1720-1725. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2022.11.17. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 36504066 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Three Neglected STARD Criteria Reduce the Uncertainty of the Liver Fibrosis Biomarker FibroTest-T2D in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD).Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 May 15;15(10):1253. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15101253. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40428246 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fremont V. Diabetes. In: Masson G., editor. Thesis French Academy of Medicine. Paris, France: 1891. p. 51.
-
- Bornstein S.R., Rubino F., Khunti K., Mingrone G., Hopkins D., Birkenfeld A.L., Boehm B., Amiel S., Holt R., Skyler J.S., et al. Practical recommendations for the management of diabetes in patients with COVID-19. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020;8:546–550. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30152-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

