Desmopressin Stimulates Nitric Oxide Production in Human Lung Microvascular Endothelial Cells
- PMID: 35327581
- PMCID: PMC8945551
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12030389
Desmopressin Stimulates Nitric Oxide Production in Human Lung Microvascular Endothelial Cells
Abstract
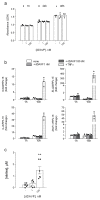
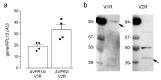
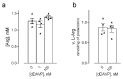
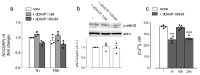
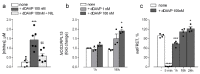
Desmopressin (dDAVP) is the best characterized analogue of vasopressin, the endocrine regulator of water balance endowed with potent vasoconstrictive effects. Despite the use of dDAVP in clinical practice, ranging from the treatment of nephrogenic diabetes insipidus to bleeding disorders, much remains to be understood about the impact of the drug on endothelial phenotype. The aim of this study was, thus, to evaluate the effects of desmopressin on the viability and function of human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (HLMVECs). The results obtained demonstrate that the vasopressor had no cytotoxic effect on the endothelium; similarly, no sign of endothelial activation was induced by dDAVP, indicated by the lack of effect on the expression of inflammatory cytokines and adhesion molecules. Conversely, the drug significantly stimulated the production of nitric oxide (NO) and the expression of the inducible isoform of nitric oxide synthase, NOS2/iNOS. Since the intracellular level of cAMP also increased, we can hypothesize that NO release is consequent to the activation of the vasopressin receptor 2 (V2R)/guanylate cyclase (Gs)/cAMP axis. Given the multifaceted role of NOS2-deriving NO for many physio-pathological conditions, the meanings of these findings in HLMVECs appears intriguing and deserves to be further addressed.
Keywords: NOS2; desmopressin; human endothelium; nitric oxide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Manning M., Misicka A., Olma A., Bankowski K., Stoev S., Chini B., Durroux T., Mouillac B., Corbani M., Guillon G. Oxytocin and vasopressin agonists and antagonists as research tools and potential therapeutics. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2012;24:609–628. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2012.02303.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

