Investigation of the Repairing Effect and Mechanism of Oral Degraded Sericin on Liver Injury in Type II Diabetic Rats
- PMID: 35327635
- PMCID: PMC8946660
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12030444
Investigation of the Repairing Effect and Mechanism of Oral Degraded Sericin on Liver Injury in Type II Diabetic Rats
Abstract
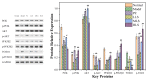
In the sericulture and silk production industry, sericin is discharged in the degumming wastewater, resulting in a large amount of wasted natural protein and environmental pollution. This study investigated the effect of degraded sericin recovered by the Ca(OH)2-ultrasound degumming method (a green process) on liver injury in T2D rats. After 4 weeks of dietary sericin supplementation, the liver masses and organ coefficients of the T2D rats improved compared with those of the model rats that were not fed sericin. Oral sericin activated the damaged PI3K/AKT/AMPK pathway to enhance glycogen synthesis, accelerate glycolysis, and inhibit gluconeogenesis. The protein expression levels of the inflammatory factors NF-κB, IL-6, and TNF-α in the T2D model group were up to two times higher than in the normal group. However, all three T2D groups that received oral sericin showed significant decreases in these factors to the level found in the normal group, indicating that inflammation in the body was significantly reduced. These results show that the sericin protein might improve glycogen synthesis, accelerate glycolysis, and inhibit gluconeogenesis by enhancing the anti-oxidation capability and reducing inflammatory reactions. Therefore, sericin recovered by Ca(OH)2 degradation has potential use in the development of functional health foods that can lower blood sugar.
Keywords: inflammatory factors; oral administration; protein expression; sericin; signaling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. The manuscript has been read and approved by all named authors, and that there are no other persons who satisfied the criteria for authorship but are not listed.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Degraded Sericin Significantly Regulates Blood Glucose Levels and Improves Impaired Liver Function in T2D Rats by Reducing Oxidative Stress.Biomolecules. 2021 Aug 23;11(8):1255. doi: 10.3390/biom11081255. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34439921 Free PMC article.
-
Silk sericin has significantly hypoglycaemic effect in type 2 diabetic mice via anti-oxidation and anti-inflammation.Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 May 1;150:1061-1071. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.10.111. Epub 2019 Nov 16. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 31743716
-
Enhancing the In Vitro Biological Activity of Degraded Silk Sericin and Its Analog Metabolites.Biomolecules. 2022 Jan 19;12(2):161. doi: 10.3390/biom12020161. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35204662 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term co-administration of sodium nitrite and sodium hydrosulfide inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis in male type 2 diabetic rats: Role of PI3K-Akt-eNOS pathway.Life Sci. 2021 Jan 15;265:118770. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118770. Epub 2020 Nov 16. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33212150
-
Sericin enhances the insulin-PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in the liver of a type 2 diabetes rat model.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Oct;16(4):3345-3352. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6615. Epub 2018 Aug 17. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30250521 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Sericin coats of silk fibres, a degumming waste or future material?Mater Today Bio. 2024 Oct 24;29:101306. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2024.101306. eCollection 2024 Dec. Mater Today Bio. 2024. PMID: 39534681 Free PMC article.
-
Silk Sericin: A Promising Sustainable Biomaterial for Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Nov 15;14(22):4931. doi: 10.3390/polym14224931. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36433058 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antidiabetic Effects of Quercetin and Silk Sericin in Attenuating Dysregulation of Hepatic Gluconeogenesis in Diabetic Rats Through Potential Modulation of PI3K/Akt/FOXO1 Signaling: In Vivo and In Silico Studies.J Xenobiot. 2025 Jan 19;15(1):16. doi: 10.3390/jox15010016. J Xenobiot. 2025. PMID: 39846548 Free PMC article.
-
Sericin-Induced Hypophagia Mediates Via M1 Muscarinic, NMDA Glutamate and Glycine Receptors in Neonatal Chicken.Arch Razi Inst. 2024 Oct 31;79(5):1109-1116. doi: 10.32592/ARI.2024.79.5.1109. eCollection 2024 Oct. Arch Razi Inst. 2024. PMID: 40292069 Free PMC article.
-
Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Nanovesicles Containing H8 Improve Hepatic Glucose and Lipid Metabolism and Exert Ameliorative Effects in Type 2 Diabetes.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Jul 3;19:6643-6658. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S455021. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38979532 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hideki U., Akira K., Yasuhiro S., Esteban C.G., Shuichi M., Kohei M., Noriko M., Nagako K., Takashi T., Yasuko H., et al. Oxidative stress is associated with adiposity and insulin resistance in men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003;88:4673–4676. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

