Endogenous Human Proteins Interfering with Amyloid Formation
- PMID: 35327638
- PMCID: PMC8946693
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12030446
Endogenous Human Proteins Interfering with Amyloid Formation
Abstract
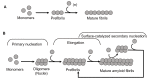
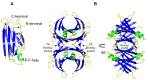
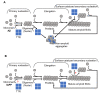
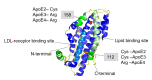
Amyloid formation is a pathological process associated with a wide range of degenerative disorders, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and diabetes mellitus type 2. During disease progression, abnormal accumulation and deposition of proteinaceous material are accompanied by tissue degradation, inflammation, and dysfunction. Agents that can interfere with the process of amyloid formation or target already formed amyloid assemblies are consequently of therapeutic interest. In this context, a few endogenous proteins have been associated with an anti-amyloidogenic activity. Here, we review the properties of transthyretin, apolipoprotein E, clusterin, and BRICHOS protein domain which all effectively interfere with amyloid in vitro, as well as displaying a clinical impact in humans or animal models. Their involvement in the amyloid formation process is discussed, which may aid and inspire new strategies for therapeutic interventions.
Keywords: BRICHOS; IAPP; alpha-synuclein; amyloid inhibition; amyloid-beta; apolipoprotein E; clusterin; endogenous proteins; transthyretin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

