PD-L1 Silencing in Liver Using siRNAs Enhances Efficacy of Therapeutic Vaccination for Chronic Hepatitis B
- PMID: 35327662
- PMCID: PMC8946278
- DOI: 10.3390/biom12030470
PD-L1 Silencing in Liver Using siRNAs Enhances Efficacy of Therapeutic Vaccination for Chronic Hepatitis B
Abstract
In chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection, virus-specific T cells are scarce and partially dysfunctional. Therapeutic vaccination is a promising strategy to induce and activate new virus-specific T cells. In long-term or high-level HBV carriers, however, therapeutic vaccination by itself may not suffice to cure HBV. One reason is the impairment of antiviral T cells by immune checkpoints. In this study, we used small-interfering RNA (siRNA) in combination with a heterologous prime-boost therapeutic vaccination scheme (TherVacB) to interfere with a major immune checkpoint, the interaction of programmed death protein-1 (PD-1) and its ligand (PDL-1). In mice persistently replicating HBV after infection with an adeno-associated virus harboring the HBV genome, siRNA targeting PD-L1 resulted in a higher functionality of HBV-specific CD8+ T cells after therapeutic vaccination, and allowed for a more sustained antiviral effect and control of HBV in peripheral blood and in the liver. The antiviral effect was more pronounced if PD-L1 was down-regulated during prime than during boost vaccination. Thus, targeting PD-L1 using siRNA is a promising approach to enhance the efficacy of therapeutic vaccination and finally cure HBV.
Keywords: HBV; PD-L1; RNAi; checkpoint inhibition; hepatitis; immunology; therapeutic vaccination.
Conflict of interest statement
U.P and A.K. are named as inventors on a patent application describing the therapeutic vaccination scheme of
Figures

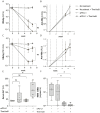

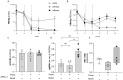
References
-
- WHO Global Progress Report on HIV, Viral Hepatitis and Sexually Transmitted Infections. 2021. [(accessed on 18 January 2022)]. Available online: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/hadle/10665/342808/9789240030985-eng.pdf.
-
- Gane E., Verdon D.J., Brooks A.E., Gaggar A., Nguyen A.H., Subramanian G.M., Schwabe C., Dunbar R. Anti-PD-1 blockade with nivolumab with and without therapeutic vaccination for virally suppressed chronic hepatitis B: A pilot study. J. Hepatol. 2019;71:900–907. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.06.028. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

