Gastroesophageal Reflux in Children with Asthma
- PMID: 35327708
- PMCID: PMC8947462
- DOI: 10.3390/children9030336
Gastroesophageal Reflux in Children with Asthma
Abstract
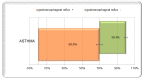
Background: Nowadays it is considered that a specific causal relationship exists between asthma and gastroesophageal reflux (GER), because of the aspiration of gastric refluate which leads to and maintain spasticity even real crisis of paroxystic expiratory dyspnea. This study explores this relationship and evaluates the results after treatment. Methods: 56 children diagnosed with asthma, hospitalized in a regional center of pediatric gastroenterology in Northeast Romania, underwent 24-hour continuous esophageal pH monitoring in order to establish the presence of GER. The Boix-Ochoa score was used to interpret the results. Proton pump inhibitors were administered to those with GER and the patients were reevaluated after 2 months. Results: 39 patients (69.64%) had GER, with a Boix-Ochoa score above normal (N < 11.99), and 17 patients (30.36%) had normal score. After administering proton pump inhibitors for 2 months, 7 patients still had high Boix-Ochoa score (17.95%). The result of this analysis shows that the presence of asthma increases the chance of GER by 2.86 times. Conclusions: In children with asthma we have to look for GER in order to treat, because it can help the treatment of asthma or even solve some cases resistant to standard treatment.
Keywords: 24 h esophageal pH-metry; Boix-Ochoa score; asthma; children; gastroesophageal reflux.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Correlation between the different pH-metry scores in gastroesophageal reflux disease in children.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Jun;95(26):e3804. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003804. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27367982 Free PMC article.
-
Is There a Potential Link between Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease and Recurrent Respiratory Tract Infections in Children?Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jul 7;13(13):2310. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13132310. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37443704 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between gastroesophageal reflux disease and recurrent wheezing in children.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Nov 24;100(47):e27660. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000027660. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 34964728 Free PMC article.
-
Cough and gastroesophageal reflux: from the gastroenterologist end.Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2009 Apr;22(2):135-8. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2008.11.007. Epub 2008 Nov 27. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2009. PMID: 19063984 Review.
-
Gastroesophageal reflux in childhood.Curr Probl Surg. 1996 Jan;33(1):1-70. Curr Probl Surg. 1996. PMID: 8536488 Review.
Cited by
-
Evidence-Based Review by a Multidisciplinary Team of Pediatricians on the Use of Gastric Acid-Reducing Medications in Children: Indian Perspectives.Cureus. 2025 May 7;17(5):e83653. doi: 10.7759/cureus.83653. eCollection 2025 May. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40486365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of the pediatric patient with asthma and obesity.Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2024 Jan;132(1):30-39. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2023.10.001. Epub 2023 Oct 10. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2024. PMID: 37827386 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current Approaches in the Multimodal Management of Asthma in Adolescents-From Pharmacology to Personalized Therapy.Biomedicines. 2023 Aug 30;11(9):2429. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11092429. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37760870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pediatric Gastroenterology Research.Life (Basel). 2023 Aug 25;13(9):1810. doi: 10.3390/life13091810. Life (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37763214 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges in the Pharmacotherapeutic Management of Pediatric Asthma.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Dec 18;15(12):1581. doi: 10.3390/ph15121581. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36559032 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kenneth R. DeVault and Donald, O. Castell. Updated Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2005;100:190–200. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources