Long Intergenic Non-Protein Coding RNA 02381 Promotes the Proliferation and Invasion of Ovarian Endometrial Stromal Cells through the miR-27b-3p/CTNNB1 Axis
- PMID: 35327987
- PMCID: PMC8955621
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13030433
Long Intergenic Non-Protein Coding RNA 02381 Promotes the Proliferation and Invasion of Ovarian Endometrial Stromal Cells through the miR-27b-3p/CTNNB1 Axis
Abstract
Purpose: Catenin Beta 1 (CTNNB1) is a key regulator of cell proliferation and invasion in endometriosis; however, its upstream factor is not clear. Long noncoding RNAs may participate in endometriosis. The aim of this study was to investigate the mechanism of interaction between LINC02381 and CTNNB1 in endometriosis.
Method: Screening and validation of RNAs were completed by whole transcriptional sequencing and qRT-PCR. The subcellular localization of LINC02381 was determined by RNA in situ hybridization and nucleo-cytoplasmic separation. Plasmids were transfected for functional experiments. Luciferase assay was used to verify the binding relationship.
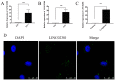
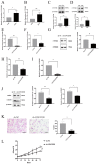
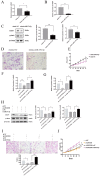
Results: The expression of LINC02381 and CTNNB1 was significantly increased in ovarian ectopic endometrial tissues (OSAs) and ectopic endometrial stromal cells (ESCs). When LINC02381 was downregulated in ESCs, the expression of CTNNB1, metallopeptidase 9 (MMP9) and cyclinD1, as well as ESCs invasion and proliferation, decreased. LINC02381 was mainly present in the cytoplasm of ESCs, indicating that it may act as a competitive endogenous RNA. Bioinformatic analysis revealed that microRNA-27b-3p (miR-27b-3p) is a downstream target of LINC02381. miR-27b-3p decreased in OSAs and ESCs. Moreover, when miR-27b-3p was upregulated in ESCs, the expression of CTNNB1, MMP9 and cyclinD1, as well as the invasion and proliferation ability of ESCs, were reduced. Additionally, rescue experiments demonstrated that the expression of CTNNB1, MMP9 and cyclinD1, as well as the invasion and proliferation ability, were significantly increased in the group transfected with both sh-LINC02381 and a miR-27b-3p inhibitor.
Conclusion: LINC02381 upregulated CTNNB1 by adsorbing miR-27b-3p, causing increased proliferation and invasion of ESCs.
Keywords: CTNNB1; LINC02381; endometriosis; invasion; miR-27b-3p; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Long non-coding RNA DHRS4 antisense RNA 1 inhibits ectopic endometrial cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in endometriosis by regulating microRNA-139-5p expression.Bioengineered. 2022 Apr;13(4):9792-9804. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2060781. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35414313 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA MALAT1 Knockdown Alleviates Fibrogenic Response in Human Endometrial Stromal Cells Via the miR-22-3p/TGFβR1/Smad2/3 Pathway.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024 Dec;82(4):3573-3584. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01445-z. Epub 2024 Aug 17. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 39154131
-
Exosomal lncRNA HOTAIR Promotes the Progression and Angiogenesis of Endometriosis via the miR-761/HDAC1 Axis and Activation of STAT3-Mediated Inflammation.Int J Nanomedicine. 2022 Mar 16;17:1155-1170. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S354314. eCollection 2022. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35321026 Free PMC article.
-
MALAT1 accelerates proliferation and inflammation and suppresses apoptosis of endometrial stromal cells via the microRNA-142-3p/CXCR7 axis.Reprod Biol. 2022 Sep;22(3):100675. doi: 10.1016/j.repbio.2022.100675. Epub 2022 Jul 25. Reprod Biol. 2022. PMID: 35901619
-
Exosomal AFAP1-AS1 binds to microRNA-15a-5p to promote the proliferation, migration, and invasion of ectopic endometrial stromal cells in endometriosis.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2022 May 5;20(1):77. doi: 10.1186/s12958-022-00942-1. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2022. PMID: 35513844 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A comprehensive overview of exosome lncRNAs: emerging biomarkers and potential therapeutics in endometriosis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jun 26;14:1199569. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1199569. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37455911 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparing gene expression in deep infiltrating endometriosis with adenomyosis uteri: evidence for dysregulation of oncogene pathways.Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2023 Apr 1;21(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12958-023-01083-9. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2023. PMID: 37005590 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs and Gene Regulatory Networks Related to Cleft Lip and Palate.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 10;24(4):3552. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043552. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of ox-LDL-induced endothelial cell injury by LINC02381 knockdown through the microRNA-491-5p/transcription factor 7 axis.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023 Mar;11(3):e785. doi: 10.1002/iid3.785. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023. PMID: 36988257 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sampson J.A. Peritoneal endometriosis due to the menstrual dissemination of endometrial tissue into the peritoneal cavity. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1927;14:422–469. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9378(15)30003-X. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

