Rif1-Dependent Control of Replication Timing
- PMID: 35328102
- PMCID: PMC8955891
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13030550
Rif1-Dependent Control of Replication Timing
Abstract
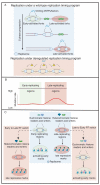
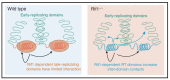
Successful duplication of the genome requires the accurate replication of billions of base pairs of DNA within a relatively short time frame. Failure to accurately replicate the genome results in genomic instability and a host of diseases. To faithfully and rapidly replicate the genome, DNA replication must be tightly regulated and coordinated with many other nuclear processes. These regulations, however, must also be flexible as replication kinetics can change through development and differentiation. Exactly how DNA replication is regulated and how this regulation changes through development is an active field of research. One aspect of genome duplication where much remains to be discovered is replication timing (RT), which dictates when each segment of the genome is replicated during S phase. All organisms display some level of RT, yet the precise mechanisms that govern RT remain are not fully understood. The study of Rif1, a protein that actively regulates RT from yeast to humans, provides a key to unlock the underlying molecular mechanisms controlling RT. The paradigm for Rif1 function is to delay helicase activation within certain regions of the genome, causing these regions to replicate late in S phase. Many questions, however, remain about the intricacies of Rif1 function. Here, we review the current models for the activity of Rif1 with the goal of trying to understand how Rif1 functions to establish the RT program.
Keywords: DNA replication; Rif1; genome stability; helicase; nuclear organization; replication timing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rif1 regulates initiation timing of late replication origins throughout the S. cerevisiae genome.PLoS One. 2014 May 30;9(5):e98501. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098501. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24879017 Free PMC article.
-
G-quadruplex binding protein Rif1, a key regulator of replication timing.J Biochem. 2021 Feb 6;169(1):1-14. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvaa128. J Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33169133 Review.
-
Budding yeast Rif1 binds to replication origins and protects DNA at blocked replication forks.EMBO Rep. 2018 Sep;19(9):e46222. doi: 10.15252/embr.201846222. Epub 2018 Aug 13. EMBO Rep. 2018. PMID: 30104203 Free PMC article.
-
Rif1 Binding and Control of Chromosome-Internal DNA Replication Origins Is Limited by Telomere Sequestration.Cell Rep. 2018 Apr 24;23(4):983-992. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.03.113. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 29694906
-
Replication timing regulation of eukaryotic replicons: Rif1 as a global regulator of replication timing.Trends Genet. 2013 Aug;29(8):449-60. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2013.05.001. Epub 2013 Jun 25. Trends Genet. 2013. PMID: 23809990 Review.
Cited by
-
The organizer of chromatin topology RIF1 ensures cellular resilience to DNA replication stress.Life Sci Alliance. 2023 Feb 6;6(4):e202101186. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202101186. Print 2023 Apr. Life Sci Alliance. 2023. PMID: 36746532 Free PMC article.
-
Replication timing and transcriptional control: beyond cause and effect - part IV.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2023 Apr;79:102031. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2023.102031. Epub 2023 Mar 9. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2023. PMID: 36905782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Origins of DNA replication in eukaryotes.Mol Cell. 2023 Feb 2;83(3):352-372. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2022.12.024. Epub 2023 Jan 13. Mol Cell. 2023. PMID: 36640769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global early replication disrupts gene expression and chromatin conformation in a single cell cycle.Genome Biol. 2022 Oct 17;23(1):217. doi: 10.1186/s13059-022-02788-7. Genome Biol. 2022. PMID: 36253803 Free PMC article.
-
R-loops acted on by RNase H1 influence DNA replication timing and genome stability in Leishmania.Nat Commun. 2025 Feb 8;16(1):1470. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-56785-y. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39922816 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

