Reduced Radiation Exposure Protocol during Computer Tomography of the Left Atrium Prior to Catheter Ablation in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation
- PMID: 35328165
- PMCID: PMC8947727
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12030612
Reduced Radiation Exposure Protocol during Computer Tomography of the Left Atrium Prior to Catheter Ablation in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
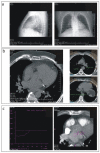
(1) Background: Computer tomography (CT) is an imaging modality used in the pre-planning of radiofrequency catheter ablation (RFA) procedure in patients with cardiac arrhythmias. However, it is associated with a considerable ionizing radiation dose for patients. This study aims to develop and validate low-dose CT scanning protocols of the left atrium (LA) for RFA guidance. (2) Methods: 68 patients scheduled for RFA of atrial fibrillation were sequentially assigned to four groups of ECG-gated scanning protocols, based on the set tube current (TC): Group A (n = 20, TC = 33 mAs), Group B (n = 18, TC = 67 mAs), Group C (n = 10, TC = 135 mAs), and control Group D (n = 20, TC = 600 mAs). We used a 256-row multidetector CT with body weight-dependent tube voltage of 80 kVp (<70 kg), 100 kVp (70−90 kg), and 120 kVp (>90 kg). We evaluated scanning parameters including radiation dose, total scanning procedure time and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). (3) Results: The average effective radiation dose (ED) was lower in Group A in comparison to Group B, C and D (0.83 (0.76−1.10), 1.55 (1.36−1.67), 2.91 (2.32−2.96) and 9.35 (8.00−10.04) mSv, p < 0.05). The total amount of contrast media was not significantly different between groups. The mean SNR was 6.5 (5.8−7.3), 7.1 (5.7−8.2), 10.8 (10.1−11.3), and 12.2 (9.9−15.7) for Group A, B, C and D, respectively. The comparisons of SNR in group A vs. B and C vs. D were without significant differences. (4) Conclusions: Optimized pre-ablation CT scanning protocols of the LA can reduce an average ED by 88.7%. Three dimensional (3D) models created with the lowest radiation protocol are useful for the integration of electro-anatomic-guided RFA procedures.
Keywords: catheter ablation; computed tomography; radiation.
Conflict of interest statement
Petr Ourednicek is a clinical scientist at Philips, Best, The Netherlands. Other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ultra-low-dose CT for left atrium and pulmonary veins imaging using new model-based iterative reconstruction algorithm.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015 Dec;16(12):1366-73. doi: 10.1093/ehjci/jev103. Epub 2015 Apr 24. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015. PMID: 25911117 Clinical Trial.
-
Left atrium and pulmonary vein imaging using sub-millisiviert cardiac computed tomography: Impact on radiofrequency catheter ablation cumulative radiation exposure and outcome in atrial fibrillation patients.Int J Cardiol. 2017 Feb 1;228:805-811. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.11.203. Epub 2016 Nov 9. Int J Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 27888758
-
Effect of automatic tube current modulation on radiation dose and image quality for low tube voltage multidetector row CT angiography: phantom study.Acad Radiol. 2009 Aug;16(8):997-1002. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2009.02.021. Epub 2009 May 5. Acad Radiol. 2009. PMID: 19409820
-
The combined application of the contrast-to-noise index and 80 kVp for cardiac CTA scanning before atrial fibrillation ablation reduces radiation dose exposure.Radiography (Lond). 2021 Aug;27(3):840-846. doi: 10.1016/j.radi.2021.01.003. Epub 2021 Feb 3. Radiography (Lond). 2021. PMID: 33549491
-
[Integration of cardiac computed tomography into pulmonary vein isolation in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation].Rofo. 2007 Dec;179(12):1264-71. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-963570. Epub 2007 Nov 14. Rofo. 2007. PMID: 18004693 German.
References
-
- Kato R., Lickfett L., Meininger G., Dickfeld T., Wu R., Juang G., Angkeow P., LaCorte J., Bluemke D., Berger R., et al. Pulmonary vein anatomy in patients undergoing catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: Lessons learned by use of magnetic resonance imaging. Circulation. 2003;107:2004–2010. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000061951.81767.4E. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Skowerski M., Wozniak-Skowerska I., Hoffmann A., Nowak S., Skowerski T., Sosnowski M., Wnuk-Wojnar A.M., Mizia-Stec K. Pulmonary vein anatomy variants as a biomarker of atrial fi-brillation—CT angiography evaluation. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2018;18:146. doi: 10.1186/s12872-018-0884-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anand R., Gorev M., Poghosyan H., Pothier L., Matkins J., Kotler G., Moroz S., Armstrong J., Nemtsov S.V., Orlov M.V. Prospective randomized comparison of rotational angiography with three-dimensional reconstruction and computed tomography merged with electro-anatomical mapping: A two center atrial fibrillation ablation study. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2016;46:71–79. doi: 10.1007/s10840-016-0111-z. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dong J., Calkins H., Solomon S.B., Lai S., Dalal D., Lardo A., Brem E., Preiss A., Berger R.D., Halperin H., et al. Integrated electroanatomic mapping with three-dimensional computed tomo-graphic images for real-time guided ablations. Circulation. 2006;113:186–194. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.565200. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

