COVI3D: Automatic COVID-19 CT Image-Based Classification and Visualization Platform Utilizing Virtual and Augmented Reality Technologies
- PMID: 35328202
- PMCID: PMC8947514
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12030649
COVI3D: Automatic COVID-19 CT Image-Based Classification and Visualization Platform Utilizing Virtual and Augmented Reality Technologies
Abstract
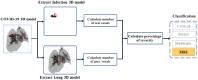
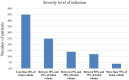
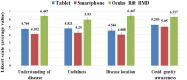
Recently many studies have shown the effectiveness of using augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) in biomedical image analysis. However, they are not automating the COVID level classification process. Additionally, even with the high potential of CT scan imagery to contribute to research and clinical use of COVID-19 (including two common tasks in lung image analysis: segmentation and classification of infection regions), publicly available data-sets are still a missing part in the system care for Algerian patients. This article proposes designing an automatic VR and AR platform for the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic data analysis, classification, and visualization to address the above-mentioned challenges including (1) utilizing a novel automatic CT image segmentation and localization system to deliver critical information about the shapes and volumes of infected lungs, (2) elaborating volume measurements and lung voxel-based classification procedure, and (3) developing an AR and VR user-friendly three-dimensional interface. It also centered on developing patient questionings and medical staff qualitative feedback, which led to advances in scalability and higher levels of engagement/evaluations. The extensive computer simulations on CT image classification show a better efficiency against the state-of-the-art methods using a COVID-19 dataset of 500 Algerian patients. The developed system has been used by medical professionals for better and faster diagnosis of the disease and providing an effective treatment plan more accurately by using real-time data and patient information.
Keywords: 3D COVID-19 visualization; augmented reality (AR); double logarithmic entropy-based segmentation; virtual reality (VR); voxel-based classification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Nextmed: Automatic Imaging Segmentation, 3D Reconstruction, and 3D Model Visualization Platform Using Augmented and Virtual Reality.Sensors (Basel). 2020 May 23;20(10):2962. doi: 10.3390/s20102962. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32456194 Free PMC article.
-
Augmented Reality Visualization for Image-Guided Surgery: A Validation Study Using a Three-Dimensional Printed Phantom.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2021 Sep;79(9):1943.e1-1943.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2021.04.001. Epub 2021 Apr 15. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2021. PMID: 34033801
-
Virtual Reality visualization for computerized COVID-19 lesion segmentation and interpretation.Biomed Signal Process Control. 2022 Mar;73:103371. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.103371. Epub 2021 Nov 24. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2022. PMID: 34840591 Free PMC article.
-
Augmented and virtual reality in spine surgery, current applications and future potentials.Spine J. 2021 Oct;21(10):1617-1625. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2021.03.018. Epub 2021 Mar 25. Spine J. 2021. PMID: 33774210 Review.
-
Presurgical and Intraoperative Augmented Reality in Neuro-Oncologic Surgery: Clinical Experiences and Limitations.World Neurosurg. 2019 Aug;128:268-276. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2019.04.256. Epub 2019 May 17. World Neurosurg. 2019. PMID: 31103764 Review.
Cited by
-
SenseCare: a research platform for medical image informatics and interactive 3D visualization.Front Radiol. 2024 Nov 21;4:1460889. doi: 10.3389/fradi.2024.1460889. eCollection 2024. Front Radiol. 2024. PMID: 39639965 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Augmented Reality Integration in Diagnostic Imaging: Myth or Reality?Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Jun 23;14(13):1333. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14131333. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39001224 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Detection and analysis of deteriorated areas in solar PV modules using unsupervised sensing algorithms and 3D augmented reality.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 16;10(6):e27973. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27973. eCollection 2024 Mar 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38532999 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive study on unraveling the advances of immersive technologies (VR/AR/MR/XR) in the healthcare sector during the COVID-19: Challenges and solutions.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 23;10(15):e35037. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35037. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39157361 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Entropy-Based Approach for Thermal Image Segmentation Using Multilevel Thresholding.Entropy (Basel). 2025 May 14;27(5):526. doi: 10.3390/e27050526. Entropy (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40422480 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Puligedda R.D., Al-Saleem F.H., Wirblich C., Kattala C.D., Jovic M., Geiszler L., Devabhaktuni H., Feuerstein G.Z., Schnell M.J., Sack M., et al. A strategy to detect emerging non-delta SARS-CoV-2 variants with a monoclonal antibody specific for the N501 spike residue. Diagnostics. 2021;11:2092. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11112092. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

