Four Types of Multiclass Frameworks for Pneumonia Classification and Its Validation in X-ray Scans Using Seven Types of Deep Learning Artificial Intelligence Models
- PMID: 35328205
- PMCID: PMC8946935
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12030652
Four Types of Multiclass Frameworks for Pneumonia Classification and Its Validation in X-ray Scans Using Seven Types of Deep Learning Artificial Intelligence Models
Abstract
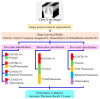
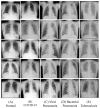
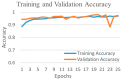
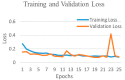
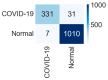
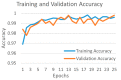
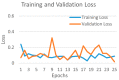
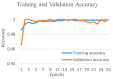
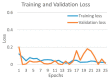
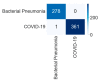
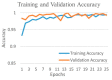
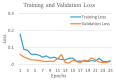
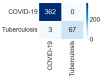
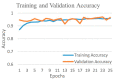
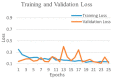
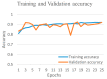
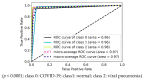
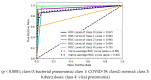
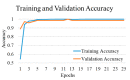
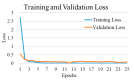
Background and Motivation: The novel coronavirus causing COVID-19 is exceptionally contagious, highly mutative, decimating human health and life, as well as the global economy, by consistent evolution of new pernicious variants and outbreaks. The reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction currently used for diagnosis has major limitations. Furthermore, the multiclass lung classification X-ray systems having viral, bacterial, and tubercular classes—including COVID-19—are not reliable. Thus, there is a need for a robust, fast, cost-effective, and easily available diagnostic method. Method: Artificial intelligence (AI) has been shown to revolutionize all walks of life, particularly medical imaging. This study proposes a deep learning AI-based automatic multiclass detection and classification of pneumonia from chest X-ray images that are readily available and highly cost-effective. The study has designed and applied seven highly efficient pre-trained convolutional neural networks—namely, VGG16, VGG19, DenseNet201, Xception, InceptionV3, NasnetMobile, and ResNet152—for classification of up to five classes of pneumonia. Results: The database consisted of 18,603 scans with two, three, and five classes. The best results were using DenseNet201, VGG16, and VGG16, respectively having accuracies of 99.84%, 96.7%, 92.67%; sensitivity of 99.84%, 96.63%, 92.70%; specificity of 99.84, 96.63%, 92.41%; and AUC of 1.0, 0.97, 0.92 (p < 0.0001 for all), respectively. Our system outperformed existing methods by 1.2% for the five-class model. The online system takes <1 s while demonstrating reliability and stability. Conclusions: Deep learning AI is a powerful paradigm for multiclass pneumonia classification.
Keywords: COVID-19; Omicron; chest X-rays; convolutional neural network; deep learning; transfer learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Segmentation-Based Classification Deep Learning Model Embedded with Explainable AI for COVID-19 Detection in Chest X-ray Scans.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Sep 2;12(9):2132. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12092132. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36140533 Free PMC article.
-
COV-RadNet: A Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Automatic Detection of COVID-19 from Chest X-Rays and CT Scans.Comput Methods Programs Biomed Update. 2022;2:100064. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpbup.2022.100064. Epub 2022 Aug 25. Comput Methods Programs Biomed Update. 2022. PMID: 36039092 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of COVID-19 in X-ray Images Using Densely Connected Squeeze Convolutional Neural Network (DCSCNN): Focusing on Interpretability and Explainability of the Black Box Model.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Dec 18;22(24):9983. doi: 10.3390/s22249983. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36560352 Free PMC article.
-
Development and integration of VGG and dense transfer-learning systems supported with diverse lung images for discovery of the Coronavirus identity.Inform Med Unlocked. 2022;32:101004. doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2022.101004. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Inform Med Unlocked. 2022. PMID: 35822170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Powerful Paradigm for Cardiovascular Risk Stratification Using Multiclass, Multi-Label, and Ensemble-Based Machine Learning Paradigms: A Narrative Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Mar 16;12(3):722. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12030722. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35328275 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Teleradiology and technology innovations in radiology: status in India and its role in increasing access to primary health care.Lancet Reg Health Southeast Asia. 2023 Apr 14;23:100195. doi: 10.1016/j.lansea.2023.100195. eCollection 2024 Apr. Lancet Reg Health Southeast Asia. 2023. PMID: 38404514 Free PMC article.
-
An Artificial Intelligence-Based Non-Invasive Approach for Cardiovascular Disease Risk Stratification in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients: A Narrative Review.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Dec 28;25(12):463. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2512463. eCollection 2024 Dec. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39742217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Confidence-Aware Severity Assessment of Lung Disease from Chest X-Rays Using Deep Neural Network on a Multi-Reader Dataset.J Imaging Inform Med. 2025 Apr;38(2):793-803. doi: 10.1007/s10278-024-01151-5. Epub 2024 Aug 20. J Imaging Inform Med. 2025. PMID: 39164451 Free PMC article.
-
Four Transformer-Based Deep Learning Classifiers Embedded with an Attention U-Net-Based Lung Segmenter and Layer-Wise Relevance Propagation-Based Heatmaps for COVID-19 X-ray Scans.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Jul 16;14(14):1534. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14141534. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061671 Free PMC article.
-
Segmentation-Based Classification Deep Learning Model Embedded with Explainable AI for COVID-19 Detection in Chest X-ray Scans.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Sep 2;12(9):2132. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12092132. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36140533 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

