COVID-19 Infection Complicated by Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation during Pregnancy-Two Cases Report
- PMID: 35328208
- PMCID: PMC8947359
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12030655
COVID-19 Infection Complicated by Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation during Pregnancy-Two Cases Report
Abstract
Coagulopathies are one of the obstetric complications affecting the period of pregnancy, childbirth, and puerperium. One of the more severe and complex disorders of the haemostatic system is the disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome (DIC), in which generalised activation of the coagulation system and activation of inflammatory cells occurs. DIC syndrome was observed in patients whose pregnancy was complicated by SARS-CoV-2 infection. Both the course of these cases and literature review indicate that particular notice should be paid to laboratory parameters of the coagulation system, closely monitoring the well-being of the foetus and, in the situation of acute DIC development, it is advised to deliver a baby and initiate intensive therapy.
Keywords: COVID-19; DIC; SARS-CoV-2; childbirth; coagulopathies; disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome; pregnancy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
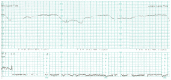
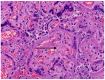
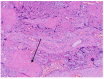
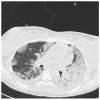
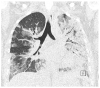
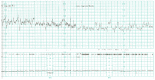
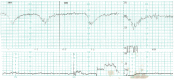
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

