A New CT Analysis of Abdominal Wall after DIEP Flap Harvesting
- PMID: 35328236
- PMCID: PMC8947670
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12030683
A New CT Analysis of Abdominal Wall after DIEP Flap Harvesting
Abstract
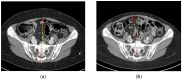
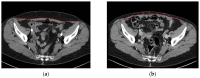
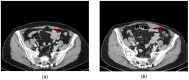
The abdominal microsurgical flap based on the deep inferior epigastric artery perforator (DIEP) flap has become the most popular option worldwide for autologous breast reconstruction. Several authors have investigated the results of reconstructed breasts, but the literature lacks systematic reviews exploring the donor site of the abdominal wall. To fulfil our aims, a new diagnostic muscle imaging analysis was designed and implemented. This study focused on rectus abdominal muscle morphology and function in a single series of 12 consecutive patients analysed before and after breast reconstruction with a microsurgical DIEP flap. Patients were divided into two groups, namely, "ipsilateral reconstruction" and "contralateral reconstruction", depending on the side of the flap harvest and breast reconstruction, then evaluated by computed tomography (CT) scans scheduled for tumor staging, and clinically examined by a physiatrist. Numerous alterations in muscle physiology were observed due to surgical dissection of perforator vessels, and rectus muscle distress without functional impairment was a common result. Postoperatively, patients undergoing "contralateral reconstruction" appeared to exhibit fewer rectus muscle alterations. Overall, only three patients were impacted by a long-term deterioration in their quality of life. On the basis of the newly developed and implemented diagnostic approach, we concluded that DIEP microsurgical breast reconstruction is a safe procedure without major complications at the donor site, even if long-term alterations of the rectus muscle are a common finding.
Keywords: CT; DIEP flap; abdominal wall; breast reconstruction; donor site morbidity; rectus muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Myosonographic evaluation of rectus abdominis muscle function after DIEP flap breast reconstruction].Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2002 Nov;34(6):386-94. doi: 10.1055/s-2002-37472. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir. 2002. PMID: 12601605 German.
-
Myosonographic study of abdominal wall dynamics to assess donor site morbidity after microsurgical breast reconstruction with a DIEP or an ms-2 TRAM flap.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2016 May;69(5):598-603. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2015.11.007. Epub 2015 Nov 25. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2016. PMID: 27049776
-
Breast reconstruction with superficial inferior epigastric artery flaps: a prospective comparison with TRAM and DIEP flaps.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004 Oct;114(5):1077-83; discussion 1084-5. doi: 10.1097/01.prs.0000135328.88101.53. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004. PMID: 15457015
-
Preoperative cross-sectional mapping for deep inferior epigastric and profunda artery perforator flaps.Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2019 Aug;9(Suppl 1):S131-S142. doi: 10.21037/cdt.2018.10.03. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2019. PMID: 31559159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Should free deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flaps be considered a quality indicator in breast reconstruction?J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2019 Dec;72(12):1923-1929. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2019.08.005. Epub 2019 Sep 7. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2019. PMID: 31570216
Cited by
-
Post-meeting report of the 2022 On-site Padua Days on Muscle and Mobility Medicine, March 30 - April 3, 2022, Padua, Italy.Eur J Transl Myol. 2022 Apr 13;32(2):10521. doi: 10.4081/ejtm.2022.10521. Eur J Transl Myol. 2022. PMID: 35421919 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Knox A.D.C., Ho A.L., Leung L., Tashakkor A.Y., Lennox P.A., Van Laeken N., Macadam S.A. Comparison of Outcomes following Autologous Breast Reconstruction Using the DIEP and Pedicled TRAM Flaps: A 12-Year Clinical Retrospective Study and Literature Review. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016;138:16–28. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000001747. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

