Comparison of CO-RADS Scores Based on Visual and Artificial Intelligence Assessments in a Non-Endemic Area
- PMID: 35328290
- PMCID: PMC8946998
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12030738
Comparison of CO-RADS Scores Based on Visual and Artificial Intelligence Assessments in a Non-Endemic Area
Abstract
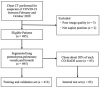
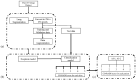
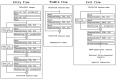
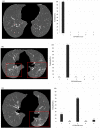
In this study, we first developed an artificial intelligence (AI)-based algorithm for classifying chest computed tomography (CT) images using the coronavirus disease 2019 Reporting and Data System (CO-RADS). Subsequently, we evaluated its accuracy by comparing the calculated scores with those assigned by radiologists with varying levels of experience. This study included patients with suspected SARS-CoV-2 infection who underwent chest CT imaging between February and October 2020 in Japan, a non-endemic area. For each chest CT, the CO-RADS scores, determined by consensus among three experienced chest radiologists, were used as the gold standard. Images from 412 patients were used to train the model, whereas images from 83 patients were tested to obtain AI-based CO-RADS scores for each image. Six independent raters (one medical student, two residents, and three board-certified radiologists) evaluated the test images. Intraclass correlation coefficients (ICC) and weighted kappa values were calculated to determine the inter-rater agreement with the gold standard. The mean ICC and weighted kappa were 0.754 and 0.752 for the medical student and residents (taken together), 0.851 and 0.850 for the diagnostic radiologists, and 0.913 and 0.912 for AI, respectively. The CO-RADS scores calculated using our AI-based algorithm were comparable to those assigned by radiologists, indicating the accuracy and high reproducibility of our model. Our study findings would enable accurate reading, particularly in areas where radiologists are unavailable, and contribute to improvements in patient management and workflow.
Keywords: artificial intelligence; coronavirus disease 2019; coronavirus disease 2019 Reporting and Data System; deep learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

