COVID-19 Diagnosis from Chest X-ray Images Using a Robust Multi-Resolution Analysis Siamese Neural Network with Super-Resolution Convolutional Neural Network
- PMID: 35328294
- PMCID: PMC8946937
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12030741
COVID-19 Diagnosis from Chest X-ray Images Using a Robust Multi-Resolution Analysis Siamese Neural Network with Super-Resolution Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract
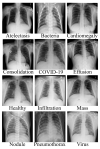
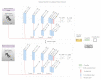
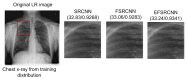
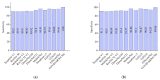
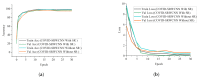
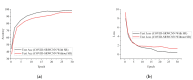
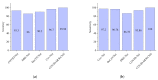
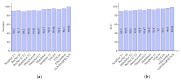
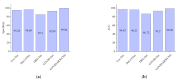
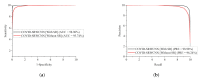
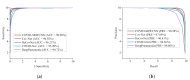
Chest X-ray (CXR) is becoming a useful method in the evaluation of coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19). Despite the global spread of COVID-19, utilizing a computer-aided diagnosis approach for COVID-19 classification based on CXR images could significantly reduce the clinician burden. There is no doubt that low resolution, noise and irrelevant annotations in chest X-ray images are a major constraint to the performance of AI-based COVID-19 diagnosis. While a few studies have made huge progress, they underestimate these bottlenecks. In this study, we propose a super-resolution-based Siamese wavelet multi-resolution convolutional neural network called COVID-SRWCNN for COVID-19 classification using chest X-ray images. Concretely, we first reconstruct high-resolution (HR) counterparts from low-resolution (LR) CXR images in order to enhance the quality of the dataset for improved performance of our model by proposing a novel enhanced fast super-resolution convolutional neural network (EFSRCNN) to capture texture details in each given chest X-ray image. Exploiting a mutual learning approach, the HR images are passed to the proposed Siamese wavelet multi-resolution convolutional neural network to learn the high-level features for COVID-19 classification. We validate the proposed COVID-SRWCNN model on public-source datasets, achieving accuracy of 98.98%. Our screening technique achieves 98.96% AUC, 99.78% sensitivity, 98.53% precision, and 98.86% specificity. Owing to the fact that COVID-19 chest X-ray datasets are low in quality, experimental results show that our proposed algorithm obtains up-to-date performance that is useful for COVID-19 screening.
Keywords: COVID-19; Siamese network; chest X-ray (CXR); convolutional neural network; multi-resolution analysis; super resolution.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest regarding this publication.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Fine-Tuned Siamese Network with Modified Enhanced Super-Resolution GAN Plus Based on Low-Quality Chest X-ray Images for COVID-19 Identification.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Mar 15;12(3):717. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12030717. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35328271 Free PMC article.
-
Chest X-ray image phase features for improved diagnosis of COVID-19 using convolutional neural network.Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2021 Feb;16(2):197-206. doi: 10.1007/s11548-020-02305-w. Epub 2021 Jan 9. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg. 2021. PMID: 33420641 Free PMC article.
-
Classification of COVID-19 pneumonia from chest CT images based on reconstructed super-resolution images and VGG neural network.Health Inf Sci Syst. 2021 Feb 20;9(1):10. doi: 10.1007/s13755-021-00140-0. eCollection 2021 Dec. Health Inf Sci Syst. 2021. PMID: 33643612 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the effect of image enhancement techniques on COVID-19 detection using chest X-ray images.Comput Biol Med. 2021 May;132:104319. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104319. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Comput Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 33799220 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 Pneumonia Classification Based on NeuroWavelet Capsule Network.Healthcare (Basel). 2022 Feb 23;10(3):422. doi: 10.3390/healthcare10030422. Healthcare (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35326900 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pathological changes or technical artefacts? The problem of the heterogenous databases in COVID-19 CXR image analysis.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2023 Oct;240:107684. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2023.107684. Epub 2023 Jun 19. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2023. PMID: 37356354 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence-assisted multistrategy image enhancement of chest X-rays for COVID-19 classification.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023 Jan 1;13(1):394-416. doi: 10.21037/qims-22-610. Epub 2022 Nov 10. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023. PMID: 36620146 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 Classification from Chest X-Ray Images: A Framework of Deep Explainable Artificial Intelligence.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022 Jul 14;2022:4254631. doi: 10.1155/2022/4254631. eCollection 2022. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35845911 Free PMC article.
-
Progressive attention integration-based multi-scale efficient network for medical imaging analysis with application to COVID-19 diagnosis.Comput Biol Med. 2023 Jun;159:106947. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.106947. Epub 2023 Apr 20. Comput Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 37099976 Free PMC article.
-
Application of artificial intelligence in 3D printing physical organ models.Mater Today Bio. 2023 Sep 15;23:100792. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2023.100792. eCollection 2023 Dec. Mater Today Bio. 2023. PMID: 37746667 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- COVID-19 Dashboard by the Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU) [(accessed on 8 June 2020)]. Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html.
-
- World Health Organization Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. [(accessed on 19 December 2021)]. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

