miR-126 Decreases Proliferation and Mammosphere Formation of MCF-7 and Predicts Prognosis of ER+ Breast Cancer
- PMID: 35328298
- PMCID: PMC8946945
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12030745
miR-126 Decreases Proliferation and Mammosphere Formation of MCF-7 and Predicts Prognosis of ER+ Breast Cancer
Abstract
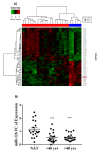
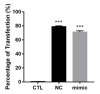
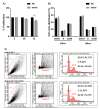
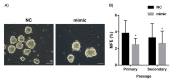
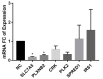
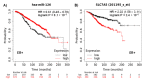
Breast cancer (BC) is a major health burden that affects over one million women each year. It is the most prevalent cancer in women and the number one cancer killer of them worldwide. Of all BC subtypes, estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) BC is the most commonly diagnosed. The objective of this study is to investigate the contribution of miR-126 in the tumorigenesis of ER+ BC. miR-126 was downregulated in ER+ BC tissues from young breast cancer patients, as shown through miRNA microarray analysis and RT-qPCR. Subsequently, the effect of the modulation of miR-126 levels on the proliferation, cell cycle progression, and spheres formation of the ER+ BC cell line, MCF-7, was assessed by MTT assay, PI analysis, and mammosphere formation assay, respectively. miR-126 overexpression significantly decreased MCF-7 proliferation and mammosphere-forming ability, but did not affect cell cycle progression. Then, in silico analysis determined SLC7A5, PLXNB2, CRK, PLK2, SPRED1, and IRS1 as potential targets of miR-126. RT-qPCR data showed that miR-126 overexpression significantly downregulated SLC7A5 and PLXNB2 mRNA levels in MCF-7. Finally, in silico survival analysis showed that high expression of miR-126 or low expression of SLC7A5 correlated with better overall survival (OS) of ER+ BC patients. Overall, our study suggests that miR-126 might play a tumor suppressor role in ER+ BC. miR-126 and SLC7A5 might also be considered potential prognostic biomarkers in ER+ BC.
Keywords: SLC7A5 (LAT1); breast cancer; estrogen receptor-positive; miR-126.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ER Negative Breast Cancer and miRNA: There Is More to Decipher Than What the Pathologist Can See!Biomedicines. 2023 Aug 18;11(8):2300. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11082300. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37626796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The combined expression of solute carriers is associated with a poor prognosis in highly proliferative ER+ breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019 May;175(1):27-38. doi: 10.1007/s10549-018-05111-w. Epub 2019 Jan 22. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019. PMID: 30671766
-
SLC7A5 serves as a prognostic factor of breast cancer and promotes cell proliferation through activating AKT/mTORC1 signaling pathway.Ann Transl Med. 2021 May;9(10):892. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-2247. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34164526 Free PMC article.
-
Estrogen receptor 1 and progesterone receptor are distinct biomarkers and prognostic factors in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer: Evidence from a bioinformatic analysis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Jan;121:109647. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109647. Epub 2019 Nov 13. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 31733575
-
Anti-miR-203 suppresses ER-positive breast cancer growth and stemness by targeting SOCS3.Oncotarget. 2016 Sep 6;7(36):58595-58605. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11193. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27517632 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs: A Link between Mammary Gland Development and Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 15;23(24):15978. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415978. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ER Negative Breast Cancer and miRNA: There Is More to Decipher Than What the Pathologist Can See!Biomedicines. 2023 Aug 18;11(8):2300. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11082300. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37626796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of the EBF1/ETS2/KLF2-miR-126-Gene Feed-Forward Loop in Breast Carcinogenesis and Stemness.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 2;26(1):328. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010328. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39796183 Free PMC article.
-
MRI-based breast cancer radiogenomics using RNA profiling: association with subtypes in a single-center prospective study.Breast Cancer Res. 2023 Jun 30;25(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s13058-023-01668-7. Breast Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37391754 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Potential of miRNAs from CSCs as an Emerging Clinical Tool for Breast Cancer Diagnosis and Prognosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 6;24(21):16010. doi: 10.3390/ijms242116010. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958993 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Howell A., Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group Tamoxifen for early breast cancer: An overview of the randomised trials. Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group. Lancet. 1998;351:1451–1467. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

