REV-ERBα Agonist SR9009 Promotes a Negative Energy Balance in Goldfish
- PMID: 35328345
- PMCID: PMC8955992
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23062921
REV-ERBα Agonist SR9009 Promotes a Negative Energy Balance in Goldfish
Abstract
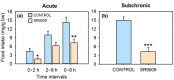
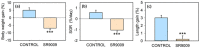
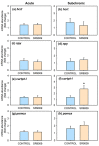
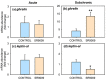
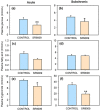
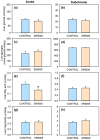
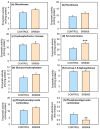
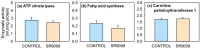
REV-ERBα (nr1d1, nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group D member 1) is a transcriptional repressor that in mammals regulates nutrient metabolism, and has effects on energy homeostasis, although its role in teleosts is poorly understood. To determine REV-ERBα's involvement in fish energy balance and metabolism, we studied the effects of acute and 7-day administration of its agonist SR9009 on food intake, weight and length gain, locomotor activity, feeding regulators, plasma and hepatic metabolites, and liver enzymatic activity. SR9009 inhibited feeding, lowering body weight and length gain. In addition, the abundance of ghrelin mRNA decreased in the intestine, and abundance of leptin-aI mRNA increased in the liver. Hypocretin, neuropeptide y (npy), and proopiomelanocortin (pomc) mRNA abundance was not modified after acute or subchronic SR9009 administration, while hypothalamic cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (cartpt-I) was induced in the subchronic treatment, being a possible mediator of the anorectic effects. Moreover, SR9009 decreased plasma glucose, coinciding with increased glycolysis and a decreased gluconeogenesis in the liver. Decreased triglyceride levels and activity of lipogenic enzymes suggest a lipogenesis reduction by SR9009. Energy expenditure by locomotor activity was not significantly affected by SR9009. Overall, this study shows for the first time in fish the effects of REV-ERBα activation via SR9009, promoting a negative energy balance by reducing energetic inputs and regulating lipid and glucose metabolism.
Keywords: body weight; feeding; fish; glucose; growth; lipids; metabolism; nr1d1.
Conflict of interest statement
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Hunter A.L., Pelekanou C.E., Adamson A., Downton P., Barron N.J., Cornfield T., Poolman T.M., Humphreys N., Cunningham P.S., Hodson L., et al. Nuclear receptor REVERBα is a state-dependent regulator of liver energy metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2020;117:25869–25879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2005330117. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

