MicroRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network Mediates Activation of mTOR and VEGF Signaling in African American Prostate Cancer
- PMID: 35328346
- PMCID: PMC8949405
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23062926
MicroRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network Mediates Activation of mTOR and VEGF Signaling in African American Prostate Cancer
Abstract
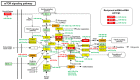
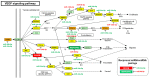
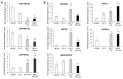
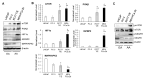
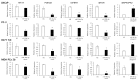
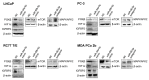
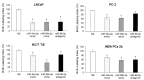
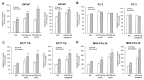
African American (AA) men exhibit 1.6-fold higher prostate cancer (PCa) incidence and 2.4-fold higher mortality rates compared to European American (EA) men. In addition to socioeconomic factors, emerging evidence suggests that intrinsic biological differences may explain part of PCa disparities. In this study, we applied microRNA (miRNA)-driven bioinformatics to evaluate whether differential miRNA-mRNA regulatory networks play a role in promoting the AA PCa disparities. 10 differentially expressed miRNAs were imported to mirPath V.3 algorithm, leading to identification of 58 signaling pathways differentially regulated in AA PCa versus EA PCa. Among these pathways, we particularly focused on mTOR and VEGF signaling, where we identified 5 reciprocal miRNA-mRNA pairings: miR-34a-5p/HIF1A, miR-34a-5p/PIK3CB, miR-34a-5p/IGFBP2, miR-99b-5p/MTOR and miR-96-5p/MAPKAPK2 in AA PCa versus EA PCa. RT-qPCR validation confirmed that miR-34a-5p, miR-99b-5p and MAPKAPK2 were downregulated, while miR-96-5p, IGFBP2, HIF1A, PIK3CB and MTOR were upregulated in AA PCa versus EA PCa cells. Transfection of miRNA mimics/antagomir followed by RT-qPCR and Western blot analysis further verified that IGFBP2, HIF1A and PIK3CB are negatively regulated by miR-34a-5p, whereas MTOR and MAPKAPK2 are negatively regulated by miR-99b-5p and miR-96-5p, respectively, at mRNA and protein levels. Targeting reciprocal pairings by miR-34a-5p mimic, miR-99b-5p mimic or miR-96-5p antagomir downregulates HIF1α, PI3Kβ, mTOR, IGFBP2 but upregulates MAPKAPK2, subsequently reducing cell proliferation and sensitizing docetaxel-induced cytotoxicity in PCa cells. These results suggest that miRNA-mRNA regulatory network plays a critical role in AA PCa disparities, and targeting these core miRNA-mRNA pairings may reduce PCa aggressiveness and overcome the chemoresistance in AA patients.
Keywords: microRNA; precision biomarker; prostate cancer disparities; reciprocal miRNA-mRNA pairing; therapeutic strategy.
Conflict of interest statement
These authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Pedroza-Torres A., Romero-Córdoba S.L., Justo-Garrido M., Salido-Guadarrama I., Rodríguez-Bautista R., Montaño S., Muñiz-Mendoza R., Arriaga-Canon C., Fragoso-Ontiveros V., Álvarez-Gómez R.M., et al. MicroRNAs in Tumor Cell Metabolism: Roles and Therapeutic Opportunities. Front. Oncol. 2019;9:1404. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01404. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

