Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Pleiotropic Impacts on Breast Cancer Occurrence, Development, and Therapy
- PMID: 35328347
- PMCID: PMC8954385
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23062927
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: Pleiotropic Impacts on Breast Cancer Occurrence, Development, and Therapy
Abstract
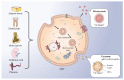
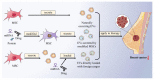
Breast cancer (BC) is one of the most devastating cancers, with high morbidity and mortality, among the female population worldwide. In BC, mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), as pluripotent stromal stem cells, play a significant role in TME formation and tumor progression. Recently, an increasing number of studies have demonstrated that extracellular vesicles (EVs) are essential for the crosstalk between MSCs and BC cells. MSC-derived EVs (MSC-EVs) can deliver a diversity of molecules, including lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, etc., to target cells, and produce corresponding effects. Studies have demonstrated that MSC-EVs exert both inhibitory and promotive effects in different situations and different stages of BC. Meanwhile, MSC-EVs provide novel therapeutic options for BC, such as EVs as carriers for drug delivery. Therefore, in this review, we summarize the role of MSC-EVs in BC progression and application in clinical treatment, in the hope of providing a basis for further research.
Keywords: breast cancer; mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles; progression; therapeutic strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- No. 31860317, No. 32160169/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- No. 20212ACB206040/Key Project of Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation
- No. 20202BAB206056/National natural science foundation of Jiangxi province
- No. XMMC-FCTM202103/Key laboratory of functional and clinical translational medicine, Fujian province university
- No. 2021CX142/the college students innovation training program of Nanchang University
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

