Dual-Function Semaphorin 4D Released by Platelets: Suppression of Osteoblastogenesis and Promotion of Osteoclastogenesis
- PMID: 35328359
- PMCID: PMC8955605
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23062938
Dual-Function Semaphorin 4D Released by Platelets: Suppression of Osteoblastogenesis and Promotion of Osteoclastogenesis
Abstract
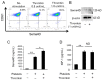
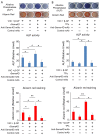
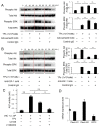
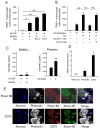
Effects of the antiosteoblastogenesis factor Semaphorin 4D (Sema4D), expressed by thrombin-activated platelets (TPs), on osteoblastogenesis, as well as osteoclastogenesis, were investigated in vitro. Intact platelets released both Sema4D and IGF-1. However, in response to stimulation with thrombin, platelets upregulated the release of Sema4D, but not IGF-1. Anti-Sema4D-neutralizing monoclonal antibody (mAb) upregulated TP-mediated osteoblastogenesis in MC3T3-E1 osteoblast precursors. MC3T3-E1 cells exposed to TPs induced phosphorylation of Akt and ERK further upregulated by the addition of anti-sema4D-mAb, suggesting the suppressive effects of TP-expressing Sema4D on osteoblastogenesis. On the other hand, TPs promoted RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis in the primary culture of bone-marrow-derived mononuclear cells (BMMCs). Among the known three receptors of Sema4D, including Plexin B1, Plexin B2 and CD72, little Plexin B2 was detected, and no Plexin B1 was detected, but a high level of CD72 mRNA was detected in RANKL-stimulated BMMCs by qPCR. Both anti-Sema4D-mAb and anti-CD72-mAb suppressed RANKL-induced osteoclast formation and bone resorptive activity, suggesting that Sema4D released by TPs promotes osteoclastogenesis via ligation to a CD72 receptor. This study demonstrated that Sema4D released by TPs suppresses osteogenic activity and promotes osteoclastogenesis, suggesting the novel property of platelets in bone-remodeling processes.
Keywords: bone regeneration; osteoblasts; osteoclasts; platelets; semaphorin 4D.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Locally Secreted Semaphorin 4D Is Engaged in Both Pathogenic Bone Resorption and Retarded Bone Regeneration in a Ligature-Induced Mouse Model of Periodontitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 18;23(10):5630. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105630. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628440 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble Sema4D cleaved from osteoclast precursors by TACE suppresses osteoblastogenesis.J Cell Mol Med. 2023 Jun;27(12):1750-1756. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17416. Epub 2023 May 11. J Cell Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37170687 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine A2A receptor (A2AR) stimulation modulates expression of semaphorins 4D and 3A, regulators of bone homeostasis.FASEB J. 2018 Jul;32(7):3487-3501. doi: 10.1096/fj.201700217R. Epub 2018 Feb 2. FASEB J. 2018. PMID: 29394106 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Semaphorin 4D in Bone Remodeling and Cancer Metastasis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018 Jun 19;9:322. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2018.00322. eCollection 2018. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2018. PMID: 29971044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Semaphorin 4D as a guidance molecule in the immune system.Int Rev Immunol. 2021;40(4):268-273. doi: 10.1080/08830185.2021.1905807. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Int Rev Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33787446 Review.
Cited by
-
Divergent associations of inflammatory markers with bone turnover markers in elderly patients with osteoporotic fractures.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 22;14(1):24907. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75704-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39438524 Free PMC article.
-
Leptin and melatonin's effects on OVX rodents' bone metabolism.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jun 27;14:1185476. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1185476. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37455920 Free PMC article.
-
Locally Secreted Semaphorin 4D Is Engaged in Both Pathogenic Bone Resorption and Retarded Bone Regeneration in a Ligature-Induced Mouse Model of Periodontitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 18;23(10):5630. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105630. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628440 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between systemic immune-inflammatory index and graded diagnosis of periodontitis: a combined cross-sectional and retrospective study.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Dec 23;24(1):1545. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-05335-x. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 39716200 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Insulin-like Growth Factor 1 on the Maintenance of Cell Viability and Osteogenic Differentiation of Gingiva-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Spheroids.Medicina (Kaunas). 2025 Jan 4;61(1):76. doi: 10.3390/medicina61010076. Medicina (Kaunas). 2025. PMID: 39859058 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

