A New Strategy for As(V) Biosensing Based on the Inhibition of the Phosphatase Activity of the Arsenate Reductase from Thermus thermophilus
- PMID: 35328363
- PMCID: PMC8949286
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23062942
A New Strategy for As(V) Biosensing Based on the Inhibition of the Phosphatase Activity of the Arsenate Reductase from Thermus thermophilus
Abstract
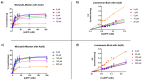
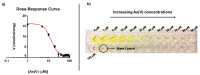
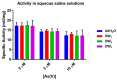
Arsenic (As) pollution is a widespread problem worldwide. In recent years, biosensors based on enzymatic inhibition have been developed for arsenic detection, making the study of the effect of inhibitors on the selected enzymatic activity crucial for their setup. The arsenate reductase of Thermus thermophilus HB27, TtArsC, reduces As(V) into As(III), but is also endowed with phosphatase activity. This work investigates the inhibitory effects of As(V) and As(III) on phosphatase activity by taking advantage of a simple colorimetric assay; the results show that both of them are non-competitive inhibitors affecting the Vmax but not the KM of the reaction. However, their Ki values are different from each other (15.2 ± 1.6 μM for As(V) and 394.4 ± 40.3 µm with As(III)), indicating a higher inhibitory effect by As(V). Moreover, the inhibition-based biosystem results to be selective for As(V) since several other metal ions and salts do not affect TtArsC phosphatase activity; it exhibits a sensitivity of 0.53 ± 0.03 mU/mg/μM and a limit of detection (LOD) of 0.28 ± 0.02 μM. The good sensitivity and specificity for As(V) point to consider inhibition of TtArsC phosphatase activity for the setup of a novel biosensor for the detection of As(V).
Keywords: Thermus thermophilus; arsenic; biosensor; thermostable arsenate reductase.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A novel arsenate reductase from the bacterium Thermus thermophilus HB27: its role in arsenic detoxification.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Oct;1834(10):2071-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2013.06.007. Epub 2013 Jun 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23800470
-
Arsenate reductase from Thermus thermophilus conjugated to polyethylene glycol-stabilized gold nanospheres allow trace sensing and speciation of arsenic ions.J R Soc Interface. 2016 Oct;13(123):20160629. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2016.0629. J R Soc Interface. 2016. PMID: 27707908 Free PMC article.
-
Self-assembling thermostable chimeras as new platform for arsenic biosensing.Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 4;11(1):2991. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-82648-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33542380 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of Thermus thermophilus ArsC enzyme and gold nanoparticles naked-eye assays speciation between As(III) and As(V).Nanotechnology. 2015 Oct 30;26(43):435703. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/26/43/435703. Epub 2015 Oct 5. Nanotechnology. 2015. Retraction in: Nanotechnology. 2023 Mar 30;34(24). doi: 10.1088/1361-6528/acc643. PMID: 26436536 Retracted.
-
Genetic identification of arsenate reductase and arsenite oxidase in redox transformations carried out by arsenic metabolising prokaryotes - A comprehensive review.Chemosphere. 2016 Nov;163:400-412. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.08.044. Epub 2016 Aug 24. Chemosphere. 2016. PMID: 27565307 Review.
Cited by
-
Extremozyme-Based Biosensors for Environmental Pollution Monitoring: Recent Developments.Biosensors (Basel). 2024 Mar 14;14(3):143. doi: 10.3390/bios14030143. Biosensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38534250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural and functional mapping of ars gene cluster in Deinococcus indicus DR1.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Dec 11;21:519-534. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.12.015. eCollection 2023. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 36618989 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbas G., Murtaza B., Bibi I., Shahid M., Niazi N.K., Khan M.I., Amjad M., Hussain M. Arsenic Uptake, Toxicity, Detoxification, and Speciation in Plants: Physiological, Biochemical, and Molecular Aspects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2018;15:59. doi: 10.3390/ijerph15010059. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

