MiR-183-5p Induced by Saturated Fatty Acids Hinders Insulin Signaling by Downregulating IRS-1 in Hepatocytes
- PMID: 35328400
- PMCID: PMC8953084
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23062979
MiR-183-5p Induced by Saturated Fatty Acids Hinders Insulin Signaling by Downregulating IRS-1 in Hepatocytes
Abstract
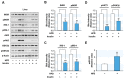
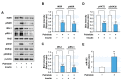
Excessive saturated fatty acids (SFA) uptake is known to be a primary cause of obesity, a widely acknowledged risk factor of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Although specific microRNAs (miRNAs) targeting insulin signaling intermediates are dysregulated by SFA, their effects on insulin signaling and sensitivity are largely unknown. Here, we investigated the role of SFA-induced miR-183-5p in the regulation of proximal insulin signaling molecules and the development of hepatic insulin resistance. HepG2 hepatocytes treated with palmitate and the livers of high-fat diet (HFD)-fed mice exhibited impaired insulin signaling resulting from dramatic reductions in the protein expressions of insulin receptor (INSR) and insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1). Differential expression analysis showed the level of miR-183-5p, which tentatively targets the 3'UTR of IRS-1, was significantly elevated in palmitate-treated HepG2 hepatocytes and the livers of HFD-fed mice. Dual-luciferase analysis showed miR-183-5p bound directly to the 3'UTR of IRS-1 and reduced IRS-1 expression at the post-transcriptional stage. Moreover, transfection of HepG2 hepatocytes with miR-183-5p mimic significantly inhibited IRS-1 expression and hindered insulin signaling, consequently inhibiting insulin-stimulated glycogen synthesis. Collectively, this study reveals a novel mechanism whereby miR-183-5p induction by SFA impairs insulin signaling and suggests miR-183-5p plays a crucial role in the pathogenesis of hepatic insulin resistance in the background of obesity.
Keywords: IRS-1; insulin resistance; miR-183-5p; obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Saturated fatty acids-induced miR-424-5p aggravates insulin resistance via targeting insulin receptor in hepatocytes.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Sep 10;503(3):1587-1593. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.07.084. Epub 2018 Jul 20. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 30033101
-
Induction of miR-96 by Dietary Saturated Fatty Acids Exacerbates Hepatic Insulin Resistance through the Suppression of INSR and IRS-1.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 30;11(12):e0169039. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169039. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 28036389 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-1271 upregulated by saturated fatty acid palmitate provokes impaired insulin signaling by repressing INSR and IRS-1 expression in HepG2 cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Sep 30;478(4):1786-91. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.09.029. Epub 2016 Sep 7. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 27613089
-
Obesity-induced miR-15b is linked causally to the development of insulin resistance through the repression of the insulin receptor in hepatocytes.Mol Nutr Food Res. 2015 Nov;59(11):2303-14. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201500107. Epub 2015 Aug 12. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2015. PMID: 26179126
-
Dietary modulation of microRNAs in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.J Nutr Biochem. 2024 Nov;133:109714. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2024.109714. Epub 2024 Aug 2. J Nutr Biochem. 2024. PMID: 39097171 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA, Insulin Resistance, and Metabolic Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 19;23(24):16215. doi: 10.3390/ijms232416215. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555853 Free PMC article.
-
The predictive function of miR-122-5p and its action mechanism by regulating PKM2 in metabolic syndrome.BMC Endocr Disord. 2025 Feb 27;25(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12902-025-01888-2. BMC Endocr Disord. 2025. PMID: 40011864 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanistic insight into the role of cardiac-enriched microRNAs in diabetic heart injury.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2025 Apr 1;328(4):H865-H884. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00736.2024. Epub 2025 Mar 4. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40033927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long Non-coding RNA SPAG5-AS1 Attenuates Diabetic Retinal Vascular Dysfunction by Inhibiting Human Retinal Microvascular Endothelial Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Tube Formation by Regulating the MicroRNA-1224-5p/IRS-1 Axis.Mol Biotechnol. 2023 Jun;65(6):904-912. doi: 10.1007/s12033-022-00572-3. Epub 2022 Nov 8. Mol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36346578
-
Potential role of microRNAs in selective hepatic insulin resistance: From paradox to the paradigm.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Nov 21;13:1028846. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1028846. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36479211 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

