Hypothyroidism and Diabetes-Related Dementia: Focused on Neuronal Dysfunction, Insulin Resistance, and Dyslipidemia
- PMID: 35328405
- PMCID: PMC8952212
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23062982
Hypothyroidism and Diabetes-Related Dementia: Focused on Neuronal Dysfunction, Insulin Resistance, and Dyslipidemia
Abstract
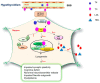
The incidence of dementia is steadily increasing worldwide. The risk factors for dementia are diverse, and include genetic background, environmental factors, sex differences, and vascular abnormalities. Among the subtypes of dementia, diabetes-related dementia is emerging as a complex type of dementia related to metabolic imbalance, due to the increase in the number of patients with metabolic syndrome and dementia worldwide. Thyroid hormones are considered metabolic regulatory hormones and affect various diseases, such as liver failure, obesity, and dementia. Thyroid dysregulation affects various cellular mechanisms and is linked to multiple disease pathologies. In particular, hypothyroidism is considered a critical cause for various neurological problems-such as metabolic disease, depressive symptoms, and dementia-in the central nervous system. Recent studies have demonstrated the relationship between hypothyroidism and brain insulin resistance and dyslipidemia, leading to diabetes-related dementia. Therefore, we reviewed the relationship between hypothyroidism and diabetes-related dementia, with a focus on major features of diabetes-related dementia such as insulin resistance, neuronal dysfunction, and dyslipidemia.
Keywords: diabetes-related dementia; dyslipidemia; hypothyroidism; insulin resistance; thyroid hormone.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hypothyroidism-Associated Dyslipidemia: Potential Molecular Mechanisms Leading to NAFLD.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 26;22(23):12797. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312797. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and intra-abdominal adiposity on the development of cardiovascular disease and diabetes mellitus.Am J Med. 2007 Mar;120(3 Suppl 1):S12-8. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2007.01.003. Am J Med. 2007. PMID: 17320517 Review.
-
Direct correlation between serum homocysteine level and insulin resistance index in patients with subclinical hypothyroidism: Does subclinical hypothyroidism increase the risk of diabetes and cardio vascular disease together?Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2018 Nov;12(6):863-867. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2018.05.002. Epub 2018 May 5. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 2018. PMID: 29748035
-
Role of ketone bodies in diabetes-induced dementia: sirtuins, insulin resistance, synaptic plasticity, mitochondrial dysfunction, and neurotransmitter.Nutr Rev. 2022 Mar 10;80(4):774-785. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuab118. Nutr Rev. 2022. PMID: 34957519 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenetic pathways of cognitive dysfunction and dementia in metabolic syndrome.Life Sci. 2019 Nov 15;237:116932. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116932. Epub 2019 Oct 10. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 31606384 Review.
Cited by
-
Thyroid functions and insulin resistance in pregnant Sudanese women.BMC Endocr Disord. 2024 Sep 27;24(1):200. doi: 10.1186/s12902-024-01739-6. BMC Endocr Disord. 2024. PMID: 39334080 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular and Neuronal Consequences of Thyroid Hormones Alterations in the Ischemic Stroke.Metabolites. 2022 Dec 23;13(1):22. doi: 10.3390/metabo13010022. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 36676947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Associations between indicators of lipid and glucose metabolism and hypothyroidism.Lipids Health Dis. 2025 Feb 18;24(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12944-025-02457-1. Lipids Health Dis. 2025. PMID: 39966896 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and pattern of cognitive dysfunction in young adults and middle-aged patients with type-2 diabetes.J Family Med Prim Care. 2025 Jun;14(6):2527-2537. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1900_24. Epub 2025 Jun 30. J Family Med Prim Care. 2025. PMID: 40726648 Free PMC article.
-
Association between pain interference and motoric cognitive risk syndrome in older adults: a population-based cohort study.BMC Geriatr. 2024 May 17;24(1):437. doi: 10.1186/s12877-024-04974-7. BMC Geriatr. 2024. PMID: 38760712 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eerdekens A., Verhaeghe J., Darras V., Naulaers G., Van den Berghe G., Langouche L., Vanhole C. The placenta in fetal thyroid hormone delivery: From normal physiology to adaptive mechanisms in complicated pregnancies. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020;33:3857–3866. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2019.1586875. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

