On the Efficacy of ZnO Nanostructures against SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 35328455
- PMCID: PMC8950216
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23063040
On the Efficacy of ZnO Nanostructures against SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
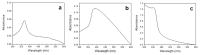
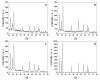
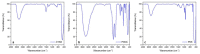
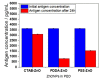
In 2019, the new coronavirus disease (COVID-19), related to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2), started spreading around the word, giving rise to the world pandemic we are still facing. Since then, many strategies for the prevention and control of COVID-19 have been studied and implemented. In addition to pharmacological treatments and vaccines, it is mandatory to ensure the cleaning and disinfection of the skin and inanimate surfaces, especially in those contexts where the contagion could spread quickly, such as hospitals and clinical laboratories, schools, transport, and public places in general. Here, we report the efficacy of ZnO nanoparticles (ZnONPs) against SARS-CoV-2. NPs were produced using an ecofriendly method and fully characterized; their antiviral activity was tested in vitro against SARS-CoV-2, showing a decrease in viral load between 70% and 90%, as a function of the material's composition. Application of these nano-antimicrobials as coatings for commonly touched surfaces is envisaged.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; antiviral; green synthesis; nano-antimicrobials; nasopharyngeal swab; nucleocapsid protein; zinc oxide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Skalny A.V., Rink L., Ajsuvakova O.P., Aschner M., Gritsenko V.A., Alekseenko S.I., Svistunov A.A., Petrakis D., Spandidos D.A., Aaseth J., et al. Zinc and respiratory tract infections: Perspectives for COVID-19 (Review) Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020;46:17–26. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4575. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Devi J. Nanoparticles as a Powerful Tool to Fight with COVID-19. Soc. Sci. Res. Netw. 2020;2020 doi: 10.2139/ssrn.3641672. - DOI
-
- Ghaffari H., Tavakoli A., Moradi A., Tabarraei A., Bokharaei-Salim F., Zahmatkeshan M., Farahmand M., Javanmard D., Kiani S.J., Esghaei M., et al. Inhibition of H1N1 influenza virus infection by zinc oxide nanoparticles: Another emerging application of nanomedicine. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019;26:70. doi: 10.1186/s12929-019-0563-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tavakoli A., Ataei-Pirkooh A., Sadeghi G.M.M., Bokharaei-Salim F., Sahrapour P., Kiani S.J., Moghoofei M., Farahmand M., Javanmard D., Monavari S.H. Polyethylene glycol-coated zinc oxide nanoparticle: An efficient nanoweapon to fight against herpes simplex virus type 1. Nanomedicine. 2018;13:2675–2690. doi: 10.2217/nnm-2018-0089. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

