Fluorescent Silica Nanoparticles Targeting Mitochondria: Trafficking in Myeloid Cells and Application as Doxorubicin Delivery System in Breast Cancer Cells
- PMID: 35328491
- PMCID: PMC8954043
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23063069
Fluorescent Silica Nanoparticles Targeting Mitochondria: Trafficking in Myeloid Cells and Application as Doxorubicin Delivery System in Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
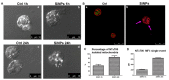
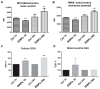
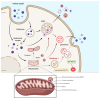
Fluorescent silica nanoparticles (SiNPs) appear to be a promising imaging platform, showing a specific subcellular localization. In the present study, we first investigated their preferential mitochondrial targeting in myeloid cells, by flow cytometry, confocal microscopy and TEM on both cells and isolated mitochondria, to acquire knowledge in imaging combined with therapeutic applications. Then, we conjugated SiNPs to one of the most used anticancer drugs, doxorubicin (DOX). As an anticancer agent, DOX has high efficacy but also an elevated systemic toxicity, causing multiple side effects. Nanostructures are usually employed to increase the drug circulation time and accumulation in target tissues, reducing undesired cytotoxicity. We tested these functionalized SiNPs (DOX-NPs) on breast cancer cell line MCF-7. We evaluated DOX-NP cytotoxicity, the effect on the cell cycle and on the expression of CD44 antigen, a molecule involved in adhesion and in tumor invasion, comparing DOX-NP to free DOX and stand-alone SiNPs. We found a specific ability to release a minor amount of CD44+ extracellular vesicles (EVs), from both CD81 negative and CD81 positive pools. Modulating the levels of CD44 at the cell surface in cancer cells is thus of great importance for disrupting the signaling pathways that favor tumor progression.
Keywords: EVs; anticancer tool; delivery system; doxorubicin; lysosomes; mitochondria; nanoparticles; theranostics.
Conflict of interest statement
Federica Sola, Chiara Barattini and Alfredo Ventola are/were employees of Aczon srl. Stefano Papa (Professor at University of Urbino) has a collaboration with Aczon srl, and Alfredo Ventola is the manager of Aczon srl. AcZon srl provided some materials needed for the study; however, AcZon srl had no influence on results generated in this work. The authors report no other potential conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures







Similar articles
-
One-pot green synthesis of doxorubicin loaded-silica nanoparticles for in vivo cancer therapy.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018 Sep 1;90:257-263. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2018.04.047. Epub 2018 Apr 17. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018. PMID: 29853089
-
99mTc-Radiolabeled Silica Nanocarriers for Targeted Detection and Treatment of HER2-Positive Breast Cancer.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Mar 8;16:1943-1960. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S276033. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33727808 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid silica-coated Gd-Zn-Cu-In-S/ZnS bimodal quantum dots as an epithelial cell adhesion molecule targeted drug delivery and imaging system.Int J Pharm. 2019 Oct 30;570:118645. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118645. Epub 2019 Aug 26. Int J Pharm. 2019. PMID: 31465835
-
Silica Nanoparticles: A Promising Vehicle for Anti-Cancer Drugs Delivery.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2025 Jan 13;26(1):33. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02982-9. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2025. PMID: 39806209 Review.
-
Silica nanoparticles in medicine: overcoming pathologies through advanced drug delivery, diagnostics, and therapeutic strategies.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2024 Apr-Jun;65(2):173-184. doi: 10.47162/RJME.65.2.03. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2024. PMID: 39020531 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular Vesicles as New Players in Drug Delivery: A Focus on Red Blood Cells-Derived EVs.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jan 21;15(2):365. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020365. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36839687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The movement of mitochondria in breast cancer: internal motility and intercellular transfer of mitochondria.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2024 Oct;41(5):567-587. doi: 10.1007/s10585-024-10269-3. Epub 2024 Mar 15. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2024. PMID: 38489056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanistic Insights into Sphingomyelin Nanoemulsions as Drug Delivery Systems for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Therapy.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Apr 2;17(4):461. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17040461. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40284457 Free PMC article.
-
Flow Cytometry and Its Applications to Molecular Biology and Diagnosis 2.0.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 11;24(22):16215. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216215. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003405 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sola F., Canonico B., Montanari M., Volpe A., Barattini C., Pellegrino C., Cesarini E., Guescini M., Battistelli M., Ortolani C., et al. Uptake and intracellular trafficking studies of multiple dye-doped core-shell silica nanoparticles in lymphoid and myeloid cells. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2021;14:29–48. doi: 10.2147/NSA.S290867. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shi M., Zhang J., Li X., Pan S., Li J., Yang C., Hu H., Qiao M., Chen D., Zhao X. Mitochondria-targeted delivery of doxorubicin to enhance antitumor activity with HER-2 peptide-mediated multifunctional pH-sensitive DQAsomes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018;13:4209–4226. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S163858. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

