Somatostatin Primes Endothelial Cells for Agonist-Induced Hyperpermeability and Angiogenesis In Vitro
- PMID: 35328517
- PMCID: PMC8949535
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23063098
Somatostatin Primes Endothelial Cells for Agonist-Induced Hyperpermeability and Angiogenesis In Vitro
Abstract
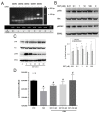
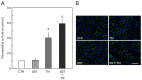
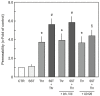
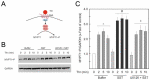
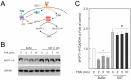
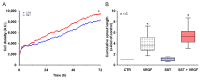
Somatostatin is an inhibitory peptide, which regulates the release of several hormones, and affects neurotransmission and cell proliferation via its five Gi protein-coupled receptors (SST1-5). Although its endocrine regulatory and anti-tumour effects have been thoroughly studied, little is known about its effect on the vascular system. The aim of the present study was to analyse the effects and potential mechanisms of somatostatin on endothelial barrier function. Cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) express mainly SST1 and SST5 receptors. Somatostatin did not affect the basal HUVEC permeability, but primed HUVEC monolayers for thrombin-induced hyperpermeability. Western blot data demonstrated that somatostatin activated the phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt) and p42/44 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways by phosphorylation. The HUVEC barrier destabilizing effects were abrogated by pre-treating HUVECs with mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase/extracellular signal regulated kinase (MEK/ERK), but not the Akt inhibitor. Moreover, somatostatin pre-treatment amplified vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-induced angiogenesis (3D spheroid formation) in HUVECs. In conclusion, the data demonstrate that HUVECs under quiescence conditions express SST1 and SST5 receptors. Moreover, somatostatin primes HUVECs for thrombin-induced hyperpermeability mainly via the activation of MEK/ERK signalling and promotes HUVEC proliferation and angiogenesis in vitro.
Keywords: Akt; MAPK; MYPT1; RhoA/Rock; angiogenesis; cAMP; endothelial permeability; somatostatin receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
P.F. is the founder and CEO of the Pharmahungary Group, a group of R&D companies (
Figures
Similar articles
-
Molecular mechanism of inhibition of the abnormal proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells by hydroxysafflor-yellow A.Pharm Biol. 2016 Sep;54(9):1800-7. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2015.1129541. Epub 2016 Jan 5. Pharm Biol. 2016. PMID: 26730646
-
Visfatin induces human endothelial VEGF and MMP-2/9 production via MAPK and PI3K/Akt signalling pathways: novel insights into visfatin-induced angiogenesis.Cardiovasc Res. 2008 May 1;78(2):356-65. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvm111. Epub 2007 Dec 18. Cardiovasc Res. 2008. PMID: 18093986
-
Effect of melatonin on EGF- and VEGF-induced monolayer permeability of HUVECs.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019 May 1;316(5):H1178-H1191. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00542.2018. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30575440
-
Role of PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK Signalling in cAMP/Epac-Mediated Endothelial Barrier Stabilisation.Front Physiol. 2019 Nov 7;10:1387. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2019.01387. eCollection 2019. Front Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31787905 Free PMC article.
-
Specific roles for the PI3K and the MEK-ERK pathway in IGF-1-stimulated chemotaxis, VEGF secretion and proliferation of multiple myeloma cells: study in the 5T33MM model.Br J Cancer. 2004 Mar 8;90(5):1076-83. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6601613. Br J Cancer. 2004. PMID: 14997210 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Review of Advances in Molecular Imaging of Rheumatoid Arthritis: From In Vitro to Clinic Applications Using Radiolabeled Targeting Vectors with Technetium-99m.Life (Basel). 2024 Jun 12;14(6):751. doi: 10.3390/life14060751. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Drought stress memory in maize: understanding and harnessing the past for future resilience.Plant Cell Rep. 2025 Apr 25;44(5):101. doi: 10.1007/s00299-025-03494-x. Plant Cell Rep. 2025. PMID: 40278890 Review.
-
Cortistatin deficiency reveals a dysfunctional brain endothelium with impaired gene pathways, exacerbated immune activation, and disrupted barrier integrity.J Neuroinflammation. 2023 Oct 4;20(1):226. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02908-5. J Neuroinflammation. 2023. PMID: 37794493 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide identification, stress- and hormone-responsive expression characteristics, and regulatory pattern analysis of Scutellaria baicalensis SbSPLs.Plant Mol Biol. 2024 Feb 16;114(2):20. doi: 10.1007/s11103-023-01410-z. Plant Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38363403 Free PMC article.
-
To grow or not to grow: the enigma of plant root growth dynamism.Plant Mol Biol. 2025 Jul 30;115(4):93. doi: 10.1007/s11103-025-01631-4. Plant Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40736880 Review.
References
-
- Schally A.V., Huang W.Y., Chang R.C., Arimura A., Redding T.W., Millar R.P., Hunkapiller M.W., Hood L.E. Isolation and structure of pro-somatostatin: A putative somatostatin precursor from pig hypothalamus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1980;77:4489–4493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4489. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Günther T., Tulipano G., Dournaud P., Bousquet C., Csaba Z., Kreienkamp H.J., Lupp A., Korbonits M., Castano J.P., Wester H.J., et al. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. CV. Somatostatin Receptors: Structure, Function, Ligands, and New Nomenclature. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018;70:763–835. doi: 10.1124/pr.117.015388. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

