A Novel Mechanism of Macrophage Activation by the Natural Yolkin Polypeptide Complex from Egg Yolk
- PMID: 35328547
- PMCID: PMC8949158
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23063125
A Novel Mechanism of Macrophage Activation by the Natural Yolkin Polypeptide Complex from Egg Yolk
Abstract
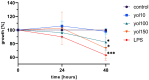
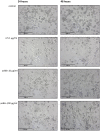
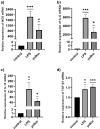
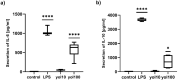
Ageing is accompanied by the inevitable changes in the function of the immune system. It provides increased susceptibility to chronic infections that have a negative impact on the quality of life of older people. Therefore, rejuvenating the aged immunity has become an important research and therapeutic goal. Yolkin, a polypeptide complex isolated from hen egg yolks, possesses immunoregulatory and neuroprotective activity. Considering that macrophages play a key role in pathogen recognition and antigen presentation, we evaluated the impact of yolkin on the phenotype and function of mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages of the BMDM cell line. We determined yolkin bioavailability and the surface co-expression of CD80/CD86 using flow cytometry and IL-6, IL-10, TGF-β and iNOS mRNA expression via real-time PCR. Additionally, the impact of yolkin on the regulation of cytokine expression by MAPK and PI3K/Akt kinases was determined. The stimulation of cells with yolkin induced significant changes in cell morphology and an increase in CD80/CD86 expression. Using pharmaceutical inhibitors of ERK, JNK and PI3K/Akt, we have shown that yolkin is able to activate these kinases to control cytokine mRNA expression. Our results suggest that yolkin is a good regulator of macrophage activity, priming mainly the M1 phenotype. Therefore, it is believed that yolkin possesses significant therapeutic potential and represents a promising possibility for the development of novel immunomodulatory medicine.
Keywords: immunomodulators; innate immunity; macrophage polarization; macrophages; yolkin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Yolkin Isolated from Hen Egg Yolk as a Natural Immunoregulator, Activating Innate Immune Response in BMDM Macrophages.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 May 15;2020:5731021. doi: 10.1155/2020/5731021. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 32509146 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of Molecular Activity of Yolkin-a Polypeptide Complex Derived from Hen Egg Yolk-in PC12 Cells and Immortalized Hippocampal Precursor Cells H19-7.Mol Neurobiol. 2023 May;60(5):2819-2831. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03246-6. Epub 2023 Feb 3. Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 36735179 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Studies of Yolkin Preparations Isolated from Egg Yolks of Selected Bird Species.Chem Biodivers. 2021 Jul;18(7):e2100178. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202100178. Epub 2021 Jun 4. Chem Biodivers. 2021. PMID: 34085749
-
Importance for humans of recently discovered protein compounds - yolkin and yolk glycopeptide 40, present in the plasma of hen egg yolk.Poult Sci. 2023 Jul;102(7):102770. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2023.102770. Epub 2023 May 3. Poult Sci. 2023. PMID: 37244087 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophage polarization and function with emphasis on the evolving roles of coordinated regulation of cellular signaling pathways.Cell Signal. 2014 Feb;26(2):192-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.11.004. Epub 2013 Nov 9. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24219909 Review.
Cited by
-
Preparation, Biological Activities, and Potential Applications of Hen Egg-Derived Peptides: A Review.Foods. 2024 Mar 14;13(6):885. doi: 10.3390/foods13060885. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38540877 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Yolkin, a Polypeptide Complex from Egg Yolk, Affects Cytokine Levels and Leukocyte Populations in Broiler Chicken Blood and Lymphoid Organs after In Ovo Administration.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 14;24(24):17494. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417494. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38139323 Free PMC article.
-
Age-Dependent Effects of Yolkin on Contact Sensitivity and Immune Phenotypes in Juvenile Mice.Molecules. 2024 Jul 10;29(14):3254. doi: 10.3390/molecules29143254. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39064833 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mine Y., Kovacs-Nolan J. New Insights in Biologically Active Proteins and Peptides Derived from Hen Egg. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2006;62:87–96. doi: 10.1079/WPS200586. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

