Specialized Proresolving Lipid Mediators: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Atherosclerosis
- PMID: 35328553
- PMCID: PMC8955102
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23063133
Specialized Proresolving Lipid Mediators: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Atherosclerosis
Abstract
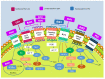
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a global public health issue due to its high morbidity, mortality, and economic impact. The implementation of innovative therapeutic alternatives for CVD is urgently required. Specialized proresolving lipid mediators (SPMs) are bioactive compounds derived from ω-3 and ω-6 fatty acids, integrated into four families: Lipoxins, Resolvins, Protectins, and Maresins. SPMs have generated interest in recent years due to their ability to promote the resolution of inflammation associated with the pathogeneses of numerous illnesses, particularly CVD. Several preclinical studies in animal models have evidenced their ability to decrease the progression of atherosclerosis, intimal hyperplasia, and reperfusion injury via diverse mechanisms. Large-scale clinical trials are required to determine the effects of SPMs in humans. This review integrates the currently available knowledge of the therapeutic impact of SPMs in CVD from preclinical and clinical studies, along with the implicated molecular pathways. In vitro results have been promising, and as such, SPMs could soon represent a new therapeutic alternative for CVD.
Keywords: atherosclerosis; inflammation; intimal hyperplasia; reperfusion injury; resolution; specialized proresolving mediators.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Resolving inflammation by using nutrition therapy: roles for specialized proresolving mediators.Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2017 Mar;20(2):145-152. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000000353. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2017. PMID: 28002074 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Specialized Pro-Resolving Lipid Mediators: New Therapeutic Approaches for Vascular Remodeling.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 25;23(7):3592. doi: 10.3390/ijms23073592. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35408952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Specialized pro-resolving mediator network: an update on production and actions.Essays Biochem. 2020 Sep 23;64(3):443-462. doi: 10.1042/EBC20200018. Essays Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32885825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resolvins as proresolving inflammatory mediators in cardiovascular disease.Eur J Med Chem. 2018 Jun 10;153:123-130. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.07.018. Epub 2017 Jul 13. Eur J Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 28732558 Review.
-
Possibility of averting cytokine storm in SARS-COV 2 patients using specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators.Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Mar;209:115437. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115437. Epub 2023 Jan 30. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36731803 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Omega-3 (n-3) Fatty Acid-Statin Interaction: Evidence for a Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease.Nutrients. 2024 Mar 27;16(7):962. doi: 10.3390/nu16070962. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38612996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gut Microbiota and Cardiovascular Diseases: Unraveling the Role of Dysbiosis and Microbial Metabolites.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 30;26(9):4264. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094264. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362500 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophage polarisation and inflammatory mechanisms in atherosclerosis: Implications for prevention and treatment.Heliyon. 2024 May 29;10(11):e32073. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32073. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38873669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Pharmacology of Inflammation Resolution in Atherosclerosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 27;23(9):4808. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094808. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resolvin D2/GPR18 signaling enhances monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cell function to mitigate abdominal aortic aneurysm formation.FASEB J. 2024 Sep 30;38(18):e70067. doi: 10.1096/fj.202400414RRR. FASEB J. 2024. PMID: 39320982
References
-
- World Health Organization Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs) [(accessed on 18 August 2021)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases...
-
- Morales Aguilar R., Lastre-Amell G., Pardo Vásquez A. Estilos de vida relacionados con factores de riesgo cardiovascular. AVFT Arch. Venez. Farm. Ter. 2018;37:50–62.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

