The Potent Phytoestrogen 8-Prenylnaringenin: A Friend or a Foe?
- PMID: 35328588
- PMCID: PMC8953904
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23063168
The Potent Phytoestrogen 8-Prenylnaringenin: A Friend or a Foe?
Abstract
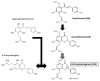
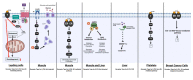
8-prenylnaringenin (8-PN) is a prenylated flavonoid, occurring, in particular, in hop, but also in other plants. It has proven to be one of the most potent phytoestrogens in vitro known to date, and in the past 20 years, research has unveiled new effects triggered by it in biological systems. These findings have aroused the hopes, expectations, and enthusiasm of a "wonder-drug" for a host of human diseases. However, the majority of 8-PN effects require such high concentrations that they cannot be reached by normal dietary exposure, only pharmacologically; thus, adverse impacts may also emerge. Here, we provide a comprehensive and up-to-date review on this fascinating compound, with special reference to the range of beneficial and untoward health consequences that may ensue from exposure to it.
Keywords: beer; flavonoids; isoxanthohumol; naringenin; natural compounds; phytoestrogens; xanthohumol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Verzele M. 100 years of hop chemistry and its relevance to brewing. J. Inst. Brew. 1986;92:32–48. doi: 10.1002/j.2050-0416.1986.tb04372.x. - DOI
-
- Goetz P. Traitement des bouffées de chaleur par insuffisance ovarienne par l’extrait de houblon (Humulus lupulus) Rev. Phytothérapie Prat. 1990;4:13–15.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

